Introduction:
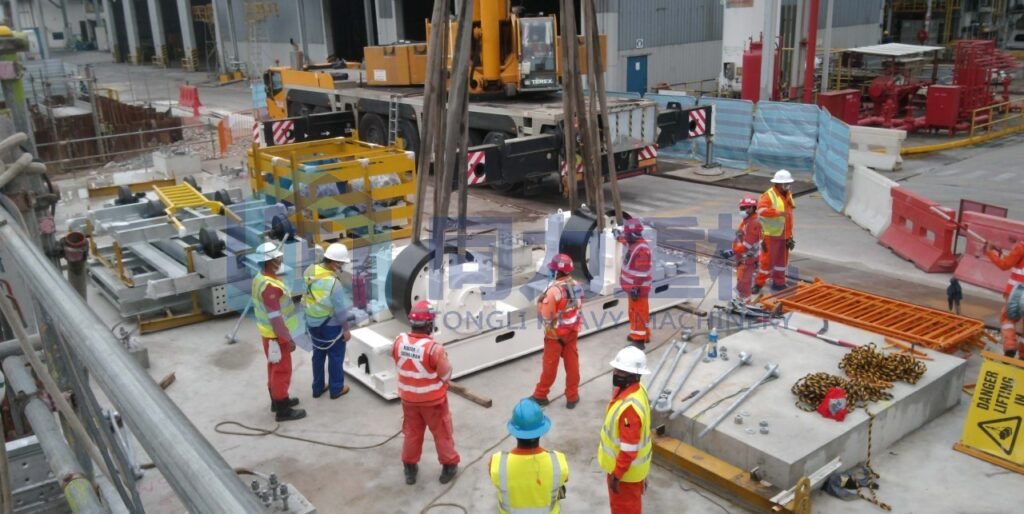
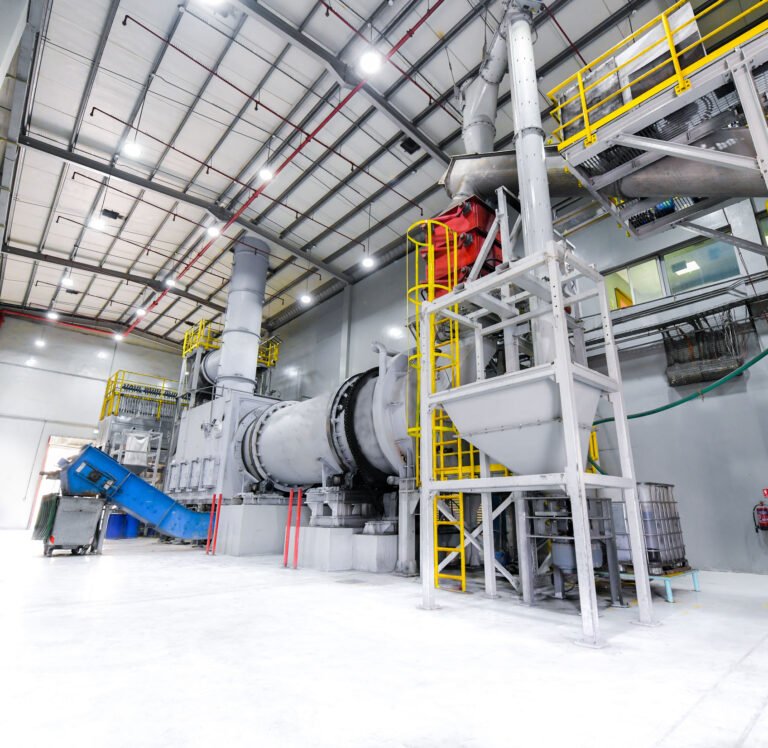
Singapore’s ECO Special Waste Management Pte Ltd operates a state-of-the-art Rotary Kiln Hazardous Waste Incineration Plant, featuring a high-temperature rotary kiln system supplied by Tongli Heavy Machinery, with integrated tail-gas treatment for environmental safety. Located within ECO’s expansive Tuas Integrated Waste Management Complex, a 7-hectare, multi-facility site with advanced capabilities such as hazardous-to-energy processing, fluidized-bed incineration, sludge treatment, and precious metal recovery—the rotary kiln treats highly toxic industrial waste by incinerating it at temperatures up to 1200 °C, drastically reducing waste volume while converting heat into usable steam and electricity via the SCC the secondary combustion chamber and waste heat boiler; meanwhile, exhaust gases are purified through desulfurization, denitrification, and particulate removal systems to ensure compliance and sustainability.
What technology is used in ECO hazardous waste incineration?
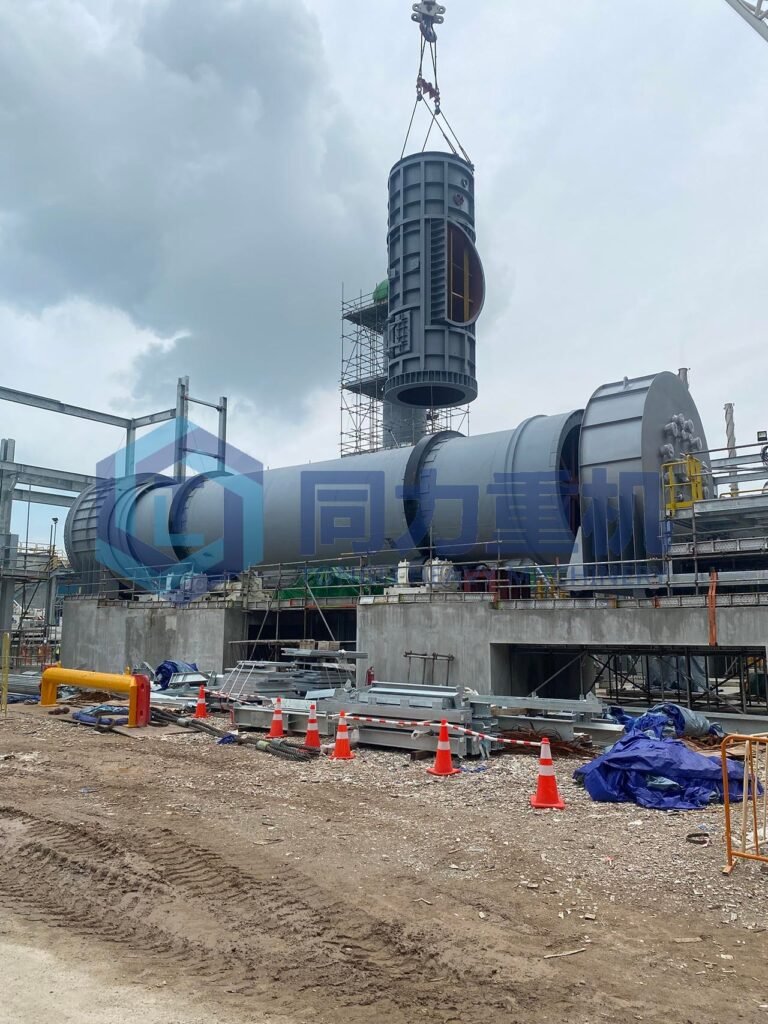

This project utilizes a combined "rotary kiln + secondary combustion chamber" incineration process. The secondary combustion chamber features a new variable-diameter design, fully utilizing high-temperature heat treatment to achieve harmless treatment and volume reduction, ensuring sufficient residence time of flue gas in the high-temperature range for the complete decomposition of toxic and hazardous substances. Regarding flue gas treatment, based on the traditional dry-wet deacidification process, this project adds a secondary wet process and an SNCR denitrification system to enhance flue gas deacidification at a low cost. Furthermore, an activated carbon fixed bed and whitening device are added to efficiently remove heavy metals and dioxins, eliminating visual pollution and ultimately achieving ultra-low flue gas emissions.
How does ECO Special Waste Management handle hazardous waste in Singapore?
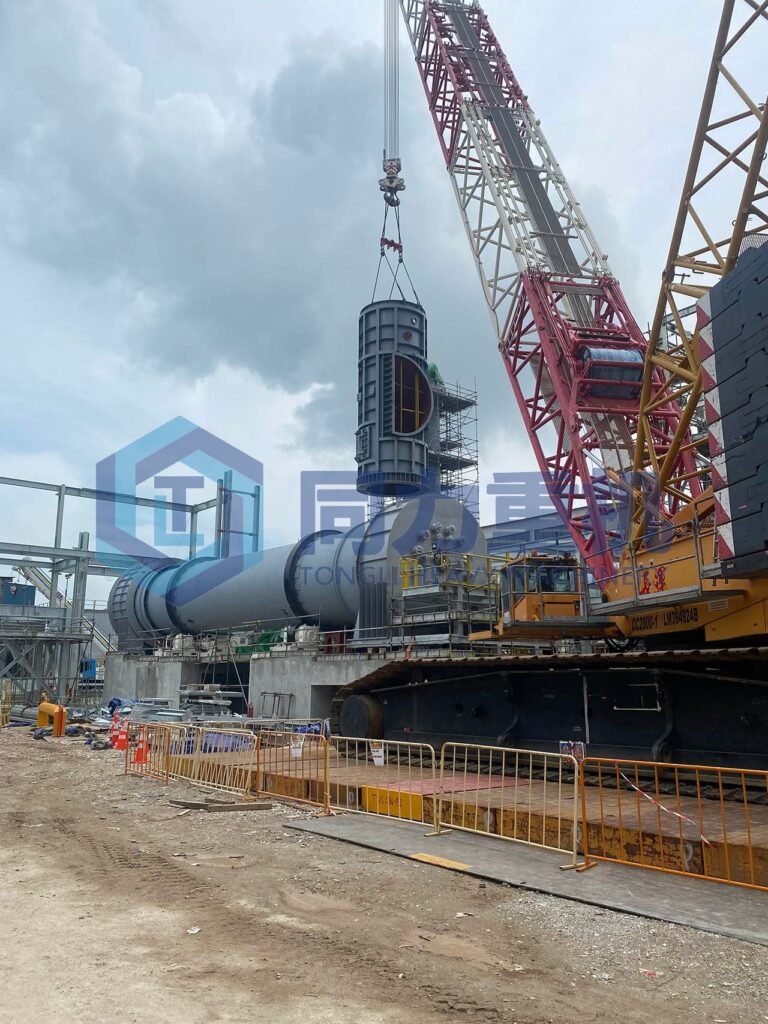

ECO operates a highly advanced, centralized facility in Tuas—comprising over 14 treatment units across 7 hectares—equipped to manage all major types of hazardous and industrial waste, including toxic industrial, sludge, biohazardous, and wastewater through integrated systems like fluidized bed incinerators, waste-to-energy incinerators, and wastewater treatment plants. At the heart of its hazardous-waste handling is the Hazardous waste Rotary Kiln Incineration Plant, which thermally destroys solid, liquid, and drummed wastes at high temperatures while enabling energy and resource recovery-specifically, APC (Air Pollution Control) systems capture heat to generate steam and electricity, and wastewater from the process is treated on-site for reuse
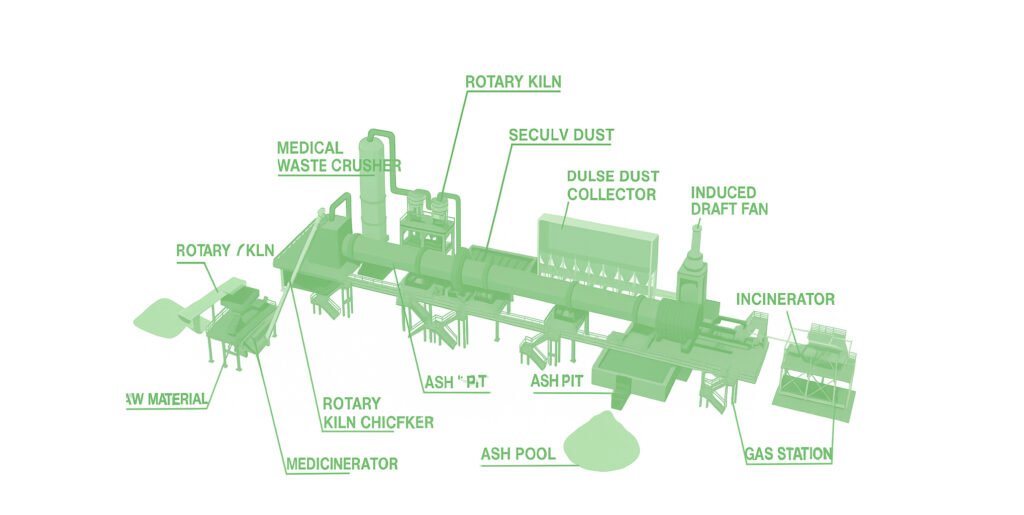
Municipal Waste Rotary Kiln: The Primary Combustion Chamber
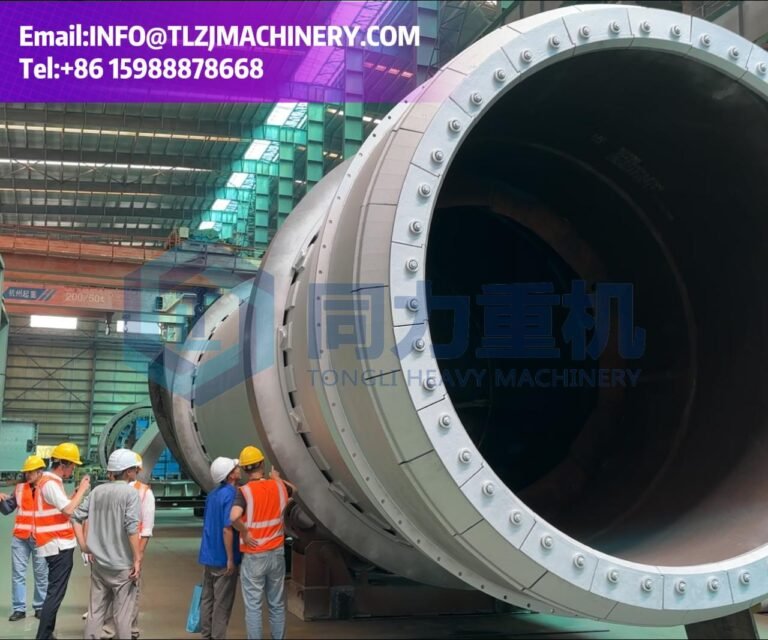
A rotary kiln is a heavy-duty, inclined, rotating cylinder, refractory-lined to resist corrosion and high heat. Wastes-solid, liquid, or containerized-are fed in; solids gradually tumble through the kiln and combust while liquids are atomized via nozzles. This tumbling and controlled rotation ensures thorough exposure to combustion temperatures 800–1,200 °C, leading to efficient breakdown of organic components, with residual non-combustibles exiting as ash.
Secondary Combustion Chamber (SCC):
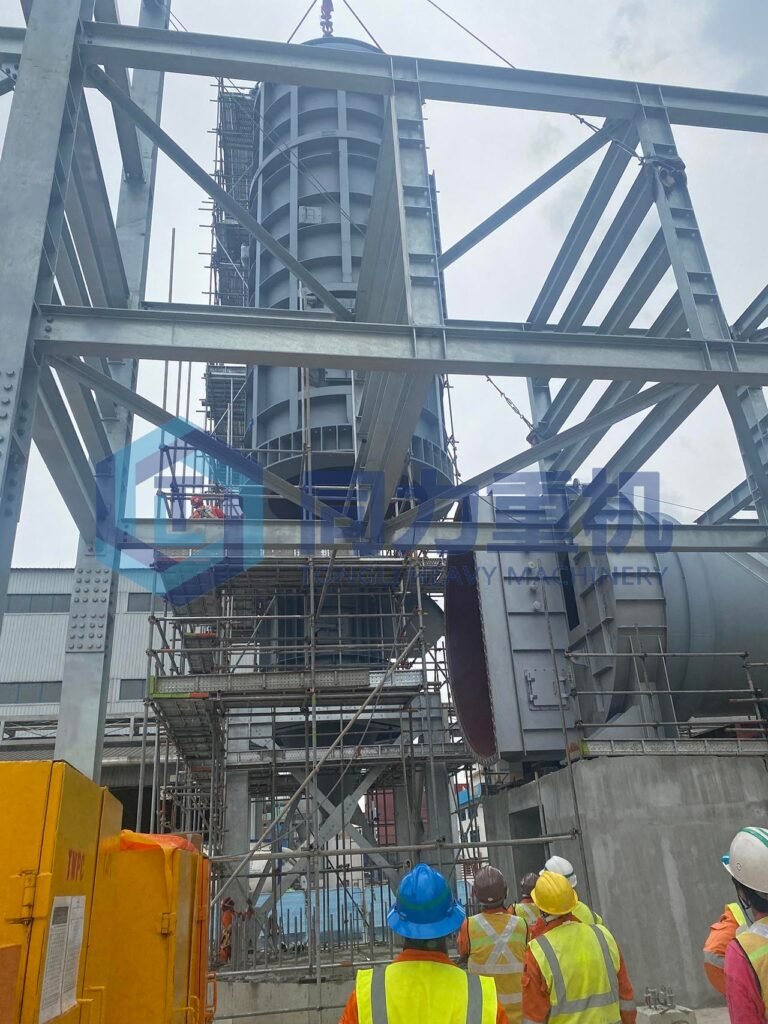

Gases and volatile compounds exiting the rotary kiln are sent to the SCC, a high-temperature afterburner designed to complete combustion-typically operating between ~1,000 and 1,200 °C, with a residence time of at least 1–3 seconds to ensure destruction of incomplete combustion products or harmful organic vapors—often achieving destruction efficiencies well above 99 %. After this, the treated gases pass through multi-stage Air Pollution Control Systems to scrub acid gases, remove particulates, trap heavy metals, and mitigate dioxin emissions before releasing them safely to the atmosphere
ECO Special Waste Management in Tuas employs a high-temperature rotary kiln incinerator to efficiently combust hazardous liquid, solid, and drum-contained wastes by tumbling them in a refractory-lined, rotating, inclined cylinder; volatile combustion products then flow into a Secondary Combustion Chamber (SCC), an afterburner maintained at 1,000–1,200 °C—that ensures thorough gas-phase combustion of any residual pollutants by providing sufficient temperature, turbulence, oxygen, and retention time; subsequently, the off-gases pass through air pollution control systems to remove acid gases, particulates, heavy metals, and dioxins, while recovering thermal energy as steam or electricity and treating process wastewater for reuse, embodying a circular, resource-efficient hazardous-waste destruction process.
How safe is ECO Special Waste Management’s hazardous waste incineration process?
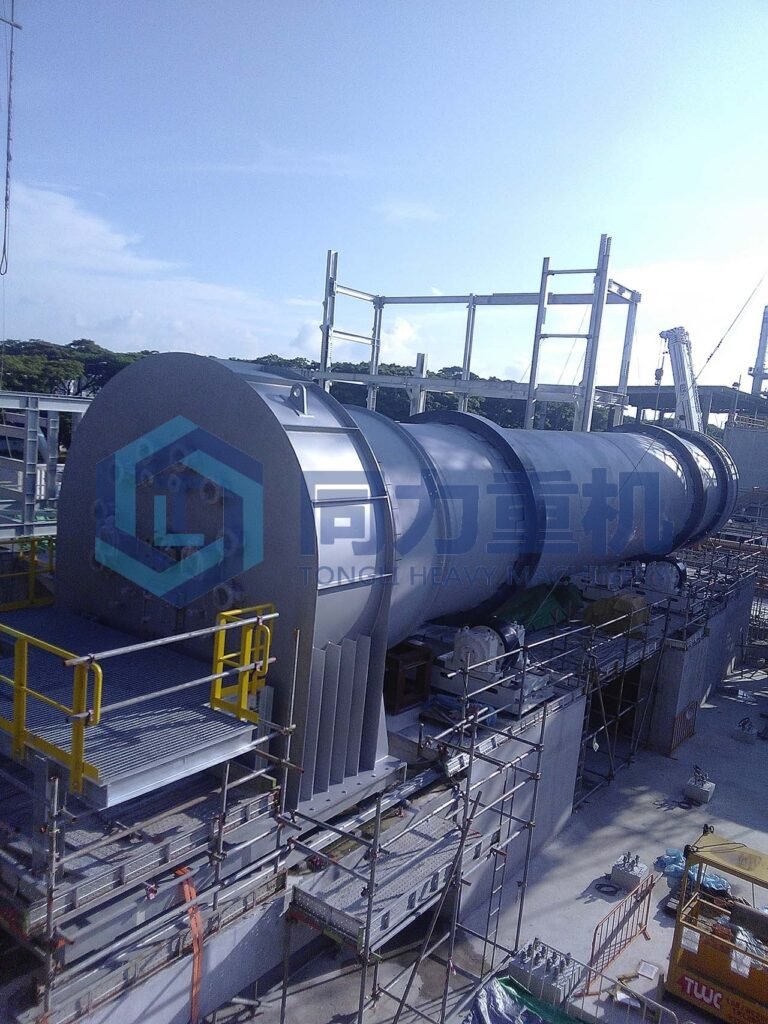

In Singapore, ECO’s hazardous-waste incineration runs under National Environment Agency (NEA) rules for special-waste incinerators that require at least 99.99% destruction/removal efficiency (DRE) for principal organic hazardous constituents and compliance with strict stack limits (e.g., particulates 50 mg/Nm³; SO₂ 200 mg/Nm³; HCl 60 mg/Nm³; HF 5 mg/Nm³; NOₓ 400 mg/Nm³). NEA also requires continuous online monitoring of key pollutants (particulates, HCl, HF, SO₂, NOₓ, CO) and continuous logging of temperatures and oxygen in the combustion zones—controls that help ensure the rotary kiln (primary chamber) and secondary combustion chamber (SCC) sustain high temperatures and adequate residence time for complete gas-phase burnout before gases enter multi-stage air-pollution control. Also the sealing of the incineration kiln has a special design it is a multile layer mechanical sealing which consisted of a rotating sealing ring and 2 fixed sealing ring with graphite sealing, becasue the whole incineration kiln operates at positive pressure, therefore the air leakage rate has cut down to less than 5%. ECO itself is NEA-licensed for toxic industrial waste and operates an ISO/IEC 17025-accredited environmental testing lab, and the company states certification to ISO 14001 (environmental), OHSAS 18001 (occupational health & safety legacy standard), and bizSAFE Star—independent signals of formal EHS management and external auditing. Taken together—regulated kiln+SCC design, CEMS oversight, tight emission caps, and third-party certifications—ECO’s process is designed to meet stringent safety and environmental performance benchmarks in Singapore.
What is The Process Flow of ECO Waste Incineration Plant?
Sorted Collection and Transportation
- The company has 180 dedicated hazardous waste recycling vehicles that comply with Singapore's Hazardous Waste Management Regulations. These vehicles are divided into 32 dedicated transport routes, each designated by hazardous waste type (e.g., HW08 waste mineral oil, HW12 dye waste, HW18 incineration residues, etc.). Each vehicle is equipped with a GPS positioning system, a double-sealed leak-proof tank (98% corrosion resistance), and an emergency adsorption device.
- The transportation process strictly adheres to "30-minute/time" real-time temperature and pressure monitoring. The transportation radius covers the entire island of Singapore and surrounding industrial areas, with a maximum daily transport volume of 450 tons. This ensures that hazardous waste transfer time from the source to the treatment plant does not exceed two hours, avoiding the risks associated with prolonged storage.

Shredding Processing
Equipped with dual-shaft shredders (160kW/unit), each with an 8m³ shredding chamber, can process all types of hazardous solid waste with a hardness of ≤HB300. Shredded particles are precisely controlled to 3-5cm, achieving a shredding efficiency of 80 tons/unit/day. Cutter wear is ≤0.2mm/day, and an automatic lubrication system extends cutter life to 1200 hours. Equipped with an "overload protection + automatic reversal" function, the machine shuts down within 0.5 seconds if unbreakable hard objects (such as rebar and alloy blocks) are encountered, preventing mechanical damage and ensuring production continuity.
Conveying Control
Three high-temperature-resistant belt conveyors, 1.2m wide and 60m long, are used (with an adjustable conveying speed of 0.8-1.2m/s). The belts are made of fluororubber and have a temperature resistance range of -40°C to 250°C, capable of withstanding a maximum material density of 2.8g/cm³. Two metal detectors (with an accuracy of ≥0.5mm) and a weight measurement system (with a measurement error of ≤±0.5%) are installed on the conveyor line to remove metal impurities in real time and precisely control the feed rate, ensuring that 30-35 tons of hazardous waste are delivered to the rotary kiln per hour, with feed stability exceeding 99%.
Rotary Kiln Incineration
The hazardous waste kiln measures 4.8m x 15m, with a 3.5° inclination angle and an adjustable rotational speed of 0.5-1.2 rpm. The kiln is constructed of high-alumina refractory bricks (refractory ≥ 1790°C) with a 200mm thick inner lining. A water cooling system (inlet water temperature 25°C, outlet water temperature ≤ 50°C) is installed on the outer wall to ensure the kiln shell temperature is ≤ 60°C. The kiln utilizes a dual-fuel heating system using natural gas and auxiliary fuel, achieving a thermal efficiency of 85%. The kiln temperature is monitored in real time by eight distributed thermocouples. The high-temperature zone (combustion section) maintains a stable temperature of 900-1100°C, with a temperature fluctuation range of ≤ ±20°C.
Stage-Based Combustion Process
- Moisture Evaporation Section (kiln head, 0-15m): Temperature 400-600°C, reducing the moisture content of hazardous waste from 15%-20% to ≤3%, with an evaporation rate of 1.2 tons/hour;
- Volatile Separation Section (15-35m): Temperature 600-800°C, achieving a 98% or higher separation rate for volatiles (such as benzene and hydrocarbons) in organic hazardous waste. Volatiles are introduced into the combustion zone via secondary air (at a speed of 8m/s);
- Complete Combustion Section (35-60m): Temperature 900-1100°C, hazardous waste residence time 65-75 minutes, organic combustible combustion efficiency ≥99.9%, CO emission concentration ≤50mg/m³;
Ash and Flue Gas Separation
The ash produced by combustion (ash content ≤5%) is discharged through a star-shaped discharge valve at the kiln tail. The ash temperature is ≤200°C, and the daily ash production is approximately The flue gas is 20 tons and has a flue gas volume of about 80,000 m³/h. It is introduced into the secondary combustion chamber through the negative pressure system at the kiln tail (negative pressure value -50Pa to -80Pa). The flue gas temperature is ≥850℃ to ensure that no harmful substances condense before entering the secondary combustion chamber.
Airflow Mixing
The secondary combustion chamber measures 5m x 8m and utilizes a "top tangential air inlet + bottom swirl air distribution" design. The secondary air velocity reaches 12m/s, creating a strong swirl flow, ensuring a flue gas-air mixing uniformity of ≥95%, preventing the formation of localized low-temperature zones. Equipped with three burners (each with a power of 200kW), it utilizes staged combustion technology and maintains an excess air coefficient of 1.2-1.3, ensuring sufficient oxygen and preventing localized high-temperature sintering.
Pyrolysis Control
The secondary combustion chamber outlet temperature is stabilized at 1100-1150°C, with temperature fluctuations controlled within ±30°C using a PID temperature control system. The flue gas residence time in the secondary combustion chamber is precisely controlled to 2.2-2.5 seconds (far exceeding the EU standard of 2 seconds). Under these conditions, the decomposition rate of dioxins is ≥99.99%, and the decomposition rate of other hazardous organic compounds (such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and halogenated hydrocarbons) is ≥99.9%. The CO concentration is reduced to ≤10mg/m³, meeting the strictest limit of Singapore's Ambient Air Quality Standards.
Flue Gas Cooling Transition
The purified flue gas passes through a rapid cooling heat exchanger (at a cooling rate of 100°C/s) from 1100°C to below 500°C, preventing the re-formation of dioxins. The heat recovery efficiency of the heat exchanger reaches 70%, and the recovered heat is used to preheat the secondary air, reducing energy consumption by approximately 15%.
Tail Exhaust gas treatment
Multi-stage dust removal system
- Cyclone dust collector: Processing air volume 80,000 m³/h, dust removal efficiency ≥90%, removes particles ≥10μm in size, outlet dust concentration ≤200 mg/m³. The ash hopper uses electric heating (temperature ≥80°C) to prevent dust agglomeration.
- Pulse bag dust collector: Filter bags are made of PTFE (temperature resistant to 260°C), filtration air velocity 0.8 m/min, pulse jet pressure 0.5-0.6 MPa, dust removal efficiency ≥99.9%, outlet dust concentration ≤10 mg/m³, and filter bag service life ≥3,000 hours.
Deep cooling and deacidification
- Multi-tube cooler: Utilizes stainless steel heat exchange tubes (Φ50 mm × 3 m) and industrial water (inlet temperature 25°C). It reduces the flue gas temperature from 500°C to 180-200°C with a cooling efficiency ≥90%. After cooling, the relative humidity of the flue gas is controlled at 40%-50%;
- Spray tower deacidification: A two-stage spray design is used. The first stage injects 20% NaOH solution (flow rate 5 m³/h) to remove acidic gases such as HCl and SO₂ (deacidification efficiency ≥ 98%). The second stage injects pure water (flow rate 3 m³/h) to remove residual alkaline mist and particulate matter. The outlet acid gas concentration is ≤ 5 mg/m³, and the droplet content is ≤ 50 mg/m³.
Final Emission Control
Exhaust gas is conveyed to a 35m high chimney via an induced draft fan (air volume 90,000 m³/h, air pressure 5,000 Pa) for discharge. An online monitoring system (CEMS) is installed at the chimney outlet to monitor dust, SO₂, NOx, CO, dioxins, and other indicators in real time. Data is uploaded to the Singapore National Environment Agency's monitoring platform every 15 minutes to ensure that all emission indicators consistently exceed national standards by at least 30%.
Who is ECO Special Waste Management Pte Ltd?

Singapore ECO Special Waste Management Pte Ltd, established in 1997, is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Beijing Capital Venture Group Co., Ltd. Headquartered at 21/23 Tuas View Ring Road, Singapore, it covers a 7-hectare site. Its extensive and specialized services encompass the treatment of toxic industrial and hazardous waste, including solutions for emerging and industry-specific difficult-to-treat waste in Singapore, separate recycling of industrial and commercial waste, safe disposal of biohazardous waste, and integrated waste management. ECO also provides services such as soil remediation, tank cleaning, asbestos investigation and removal, underground cesspool cleaning and decontamination, and the destruction of products, goods, and equipment (including intellectual property-sensitive waste) in accordance with the New Economic and Trade Agreement (NEA). In terms of hardware facilities and processing capabilities, the company operates an integrated special waste management center (comprising nine major treatment and recycling facilities) and is equipped with a fleet of over 30 waste collection vehicles and over 200 ISO tankers, open-top containers, compactors, vacuum tankers, etc., ensuring the timely and safe collection and treatment of waste. Currently, the company serves over 2,000 customers.
Who is Beijing Capital Venture Group Co., Ltd
Beijing Capital Venture Group Co., Ltd is a large state-owned enterprise established in 1994 under the supervision of the Beijing Municipal SASAC. With total assets exceeding RMB 180 billion, the group operates across four major sectors: environmental protection (water services, waste treatment, pollution control), infrastructure (roads, rail, and metro investment, including partnerships in the Beijing Subway), real estate (via its Hong Kong-listed arm Beijing Capital Land Ltd.), and financial services (investment funds and financing platforms). Headquartered in Beijing, the company has expanded both domestically and overseas, serving over 20 million people, and its subsidiaries are listed in Hong Kong, Shanghai, and Shenzhen, with an international credit rating of BBB- (Fitch).
Who is French Séché Environnement Group
Since ECO is aqquired by Séché Environnement Group we also introduce about this company a little bit in here: Séché Environnement Group is a leading French company in the environmental services sector. It is a family - owned industrial group founded in 1985, with its headquarters in Changé, France. The group specializes in the treatment and recovery of all types of waste, including complex and hazardous waste, as well as pollution control operations. It has more than 35 years of experience in industrial and territorial ecology, and its unique technologies are applied in more than 100 locations worldwide, including 40 in France. Séché Environnement Group has approximately 5,900 employees, 2,000 of whom are in France. In 2020, the company achieved sales of 675 million euros, with 25% of its revenue coming from international markets. The group is committed to creating circular economy loops, treating pollutants and greenhouse gases, and controlling hazardous substances, thereby directly contributing to the protection of life and biodiversity. For example, in 2025, the Séché Urgences Interventions team of the group completed a large - scale dismantling and management operation for waste and fire residues, neutralizing, securing, and treating more than 4,500 tons of post - fire residues from a major disaster area. In addition, at the 5th International PFAS Congress held in Paris in June 2025, Séché Environnement presented an innovative study for the Professional Syndicate for the Recycling, Valorization, Regeneration, and Treatment of Dangerous Wastes, aiming to combat "eternal pollutants".
Why did Séché Environnement acquire ECO Special Waste Management in 2024?
For 4 reasons I would say:
- The first one is to expand their business: Séché Environnement’s Spent approximately S$605 million about USD 447 million becasue they want to establish a cornorstone in the dynamic Asia-Pacific hazardous waste market—a region where the group previously had no presence.
- Secondly, Séché significantly enhanced its regional scale and profitability by accquiring Eco, ECO is the leading operator in Singapore’s hazardous industrial waste sector—with approximately 32% market share, robust 2023 sales of S$96 million, and adjusted EBITDA of S$41 million. SO it is a good idea.
- Thrid, Eco just built the waste incineration plant complex using Tongli rotary kiln and SCC in 2024, the whole factory is brand new. ECO’s expansive single-site facility (68,400 m²) houses complementary technologies—such as incinerators with and without energy recovery, stabilization units, and industrial wastewater treatment—and provides comprehensive hazardous waste services across collection, transportation, recovery, and treatment. The company also holds strategic joint ventures in activated carbon reactivation and precious metal regeneration, further reinforcing its leadership in the circular economy.
So to sum up, Maxime Séché, CEO of Séché Environnement, described the deal as a “rare opportunity to invest in a regional leader”, enabling the company to serve a strong industrial clientele in a high-growth region and to use ECO as a platform for accelerating growth across its core businesses, from environmental services and hazard management to the circular economy in Southeast Asia.
What industries rely on ECO Special Waste Management’s services?

Petrochemical Industry(Mainly)
Petrochemical plants generate large volumes of hazardous by-products in Singapre, including contaminated sludges, catalysts, and chemical residues. ECO provides safe incineration through its rotary kiln system, which is capable of destroying highly toxic hydrocarbons and chemical waste at extremely high temperatures. In addition, its secondary combustion chamber ensures complete breakdown of complex molecules, preventing the release of harmful pollutants. This makes ECO a trusted partner for petrochemical companies operating in Singapore’s industrial hubs.
Pharmaceutical and Life Sciences
Pharmaceutical manufacturing and life science research generate wastes that often contain active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), solvents, and biohazardous materials. ECO helps these industries manage sensitive waste streams through secure collection, controlled incineration, and regulatory-compliant disposal. Its high-temperature incineration ensures the destruction of pharmaceutical compounds and pathogens, protecting both public health and the environment.
Aerospace and Marine
Both the aerospace and marine sectors rely on ECO for handling hazardous maintenance waste such as solvents, paints, oils, and chemical cleaning agents. ECO’s integrated waste treatment services—including incineration, neutralization, and sludge management—allow these industries to dispose of materials safely and in compliance with international environmental regulations. The company also supports shipyards and airlines with scheduled waste collection and specialized treatment.
Oil & Gas and Power Generation
ECO supports the oil & gas and energy sectors, which produce petroleum sludges, drilling waste, oily residues, and contaminated filters. Its rotary kiln specially crafted by tongli heavy machinery is particularly suited for treating these hydrocarbon-heavy wastes, ensuring complete combustion and minimizing the risk of harmful emissions. Additionally, ECO’s energy recovery systems capture heat generated from incineration, feeding it back into the treatment process and reducing reliance on external energy sources.
Electronics and Semiconductor
The electronics and semiconductor industries create highly specialized waste streams such as spent solvents, acids, metal-bearing sludge, and e-waste residues. ECO supports these industries with advanced chemical treatment facilities and precious metal recovery systems, allowing for the recycling of valuable metals like gold, silver, and platinum from circuit boards and residues. This not only reduces hazardous waste but also contributes to circular economy goals.
Hospital and Institutions
Institutional clients such as hospitals, virus research labs, and universities often generate diverse hazardous wastes—ranging from laboratory chemicals to asbestos-containing materials. ECO provides tailored collection, analysis, and treatment solutions, including specialized laboratory services that classify and test wastes before treatment. For institutions dealing with biomedical or research-related hazardous waste, ECO ensures secure destruction and full traceability to meet strict compliance standards.
How important is ECO Special Waste Management to Singapore’s waste ecosystem?

Singapore takes the management of hazardous and industrial waste extremely seriously. This is evident from the robust laws, regulatory frameworks, and enforcement measures in place:
Legal and regulatory framework
Singapore maintains rigorous controls over hazardous waste under a range of statutes: The Environmental Public Health Act (EPHA) and supporting regulations—including the Toxic Industrial Waste Regulations—govern collection, treatment, disposal, and licensing of both general and toxic industrial waste. The National Environment Agency (NEA) oversees implementation and enforcement.
- Under the Environmental Public Health Act (EPHA), illegal dumping in public places may lead to a first-time fine of up to S$50,000, up to 12 months in jail, or both. Repeat offenders face fines up to S$100,000 and mandatory jail time.
- Under the Sewerage and Drainage (Trade Effluent) Regulations, firms discharging hazardous substances into public sewers can face fines up to S$15,000 and/or up to three months in jail.
- Additionally, via the Sewerage and Drainage Act, offenders may be fined up to S$50,000 or imprisoned up to 12 months for the first offense, with steeper penalties for repeat offenses.
Ongoing legislative upgrades
The proposed Environment Protection Legislation Amendment Bill (2024) would significantly increase penalties — doubling them for many environmental offenses. For instance:
- Tier 1 offenses: individual maximum fines up to S$2M; corporate fines up to S$10M
- Asbestos-related waste offenses: individual fines up to S$1M; corporate fines up to S$4M.
Active enforcement and monitoring
Agencies like PUB (Public Utilities Board) and NEA (National Environment Agency) use online sensors, surprise inspections, and sampling regimes. PUB, for example, monitors more than 5,000 companies annually for regulated trade effluent discharges.
Real-world examples
- Century Water Systems was fined S$3,300 for dumping dimethylacetamide into sewers—risking disruptions to NEWater facilities.
- Chem-Solv Technologies and NSL OilChem Logistics were fined S$8,500 and S$13,000 respectively for discharging banned volatile compounds and excessive heavy metals.
These heavy sanctions reflect Singapore’s high standards—contamination endangers public health, pollutes waterways, and disrupts precious water reclamation systems like NEWater.
Why Singapore Relies on Companies like ECO Special Waste Management

Singapore’s waste landscape is marked by limited land space, industrial complexity, and environmental ambitions—necessitates capable partners:
Land constraints & circular economy goals
With only one active landfill and a goal to reduce waste to landfill by 30% and raise recycling to 70% by 2030, Singapore must maximize incineration and resource recovery. Projects like Tuas Nexus integrate sludge incineration and energy recovery, saving CO₂ emissions and generating carbon credits—efforts in which ECO is involved.
Handling complex industrial waste
As manufacturing processes become more advanced, wastewater streams are chemically more complex. Licensed specialists are critical to ensure safe treatment and disposal. ECO provides customized, compliant solutions essential for water security.
Scale, licensing, and expertise
ECO boasts fully licensed facilities-handling toxic and general industrial waste, bio-hazardous waste, asbestos, etc.-supported by ISO 14001, OHSAS 18001, and BizSAFE certifications.
Public-private cooperation model
Singapore's waste ecosystem relies on private-sector firms to handle collection, treatment, and disposal, allowing the government to focus on oversight, policy, and environmental sustainability. This aligns with the "3P Partnership" model in the Singapore Green Plan 2030—a collaborative approach involving people, private sector, and government.
ECO Special Waste Management’s role and contributions
It’s worth touching on ECO’s specific contributions to highlight why Singapore leans on them:
- ECO manages over 10,000 tonnes of toxic industrial waste per month, making it one of Singapore’s largest such operators.
- The firm incorporates digital control systems, waste-to-energy, sludge treatment, and chemical recovery—all aimed at resource efficiency and circularity.
- Operating since 1997 and serving over 2,000 clients—from pharmaceuticals to aerospace—ECO has built long-term trust.
- In 2017, a flash fire due to unsafe handling of hexane resulted in a S$230,000 fine from MOM. This underscores the high regulatory and safety standards companies like ECO must uphold.
History Development Timeline of ECO Special Waste Management Pte Ltd.

Founded in 1997 July 14th
Founded in 1997, ECO Special Waste Management Pte Ltd is a private company limited by shares, and its registered address is 23 Tuas View Circuit, Eco-SWM Complex, It quickly became Singapore’s leading hazardous waste provider—licensed by the National Environment Agency to handle toxic industrial and general waste, sludge, bio-hazardous waste, and asbestos removal, with capabilities for sludge treatment up to 570 tonnes per day, serving over 2,000 clients across petrochemical, pharmaceutical,semiconductor, aerospace, marine, power generation, and life science industries.
In 2015 Acquired By Beijing Capital Group
In August 2015, Beijing Capital Private Equity a subsidiary of Beijing Capital Group acquired ECO from Navis Capital Partners for S$246 million (~US$181 million), marking its strategic expansion into regional environmental services. Under Beijing Capital’s ownership, ECO maintained its dominance in Singapore’s hazardous waste market—boasting approximately 32% market share, operating a 68,400 m² facility with integrated incinerators, stabilization plants, wastewater treatment infrastructure, and an annual capacity of nearly 440,000 tonnes.
In June 2024 Acquired by Séché Environnement Group
Finally, in June 2024, Beijing Capital sold 100% of its stake in ECO to French waste management group Séché Environnement for approximately S$605 million, receiving strong interest from global infrastructure investors and solidifying a profitable exit after nearly a decade of ownership.
is ECO Special Waste Management considered a market leader in hazardous waste?
ECO is a leading player in the hazardous waste segment, holding around 32% market share in Singapore’s hazardous waste recovery and treatment sector as of 2023 - Reuters
How does ECO Special Waste Management compare with other hazarous waste treatment processing firms in Singapore?

Like we mentioned before ECO takes about 32% of the martket share, the rest belongs to the companies listed below:
| Company | Scope & Strengths | Position Relative to ECO |
| Sembcorp Environmental Management | Integrated utilities and solid waste management, with large-scale operations in NEWater, electricity, and energy sectors. | Focused more on municipal and commercial waste and utilities—less on specialized hazardous waste treatment. |
| Veolia ES Singapore | Global environmental services provider—covers general and hazardous waste, wastewater, incineration, waste-to-energy, landfill operations. | Strong competitor with broader service offerings; ECO holds a deeper niche in hazardous waste. |
| Colex Holdings, Recycling Partners, 800 Super, etc. | Serve solid, recyclable, and municipal waste segments. Specialized stream recycling and collection. | ECO differentiates through hazardous waste treatment capacity and infrastructure. |
| Other General Service Providers (e.g., Wah & Hua, Crimson, V8 Environmental) | Provide general, construction, or commercial waste collection/disposal. | These firms focus on front-line logistics rather than high-complexity hazardous-waste technologies. |
1. Veolia ES Singapore
A subsidiary of global giant Veolia Environmental Services, it offers comprehensive environmental servicesincluding collection, advanced treatment, and incineration of both general and hazardous waste as well as wastewater processing and energy recovery solutions. Veolia brings mature, global technical know-how to the local market.
2. Sembcorp Environmental Management (SembWaste)
A major local player, Sembcorp’s waste arm focuses on municipal and solid waste management, energy recovery (Waste-to-Resource), and NEWater production. It integrates utility-scale operations with broader environmental services.
3. Colex Holdings Limited
Known for waste recycling—particularly of packaging and plastics—Colex complements resource recovery and recycling efforts across commercial and industrial clients. While active in the broader waste sector, it’s less focused on hazardous waste treatment.
4. Recycling Partners Pte. Ltd.
Specializes in recycling and waste collection services. It’s part of the broader waste chain in Singapore, focusing on resource recovery and recycling customer demands.
5. Pride-Chem
A niche player licensed by the NEA for treating chemical and industrial hazardous wastes. Its portfolio includes spent cupric chloride, etchants, spent acids, and contaminated drums—targeting specialized chemical-process waste streams.
6. Tidy Waste Management Group (Tidychem)
A recognized toxic waste collector under NEA, Tidychem is particularly strong in solvent recovery and distillation. In 2022, they recycled 99.4% of 1,303 tonnes of hazardous solvents—highlighting strong circularity in solvent handling.
7. Environmental Solutions Asia
A local specialist in chemical, physical, and thermal treatment of hazardous waste—especially spent catalysts, acids and alkalis—from industries such as semiconductors and petrochemicals. The company also engages in resource recovery of base/precious metals.
8. Belfor Singapore
Focused on post-disaster hazardous waste management and industrial decontamination (e.g., fire or flood incidents). Their services are tailored for acute incident-related cleanup rather than ongoing industrial hazardous waste operations.
9. Cramoil Chemical Corporation
An established specialty chemical manufacturer (founded in 1982) that also manages its own chemical waste streams. They handle spent solvents, scrubber water, lubricants, and monomer residues—particularly relevant to chemical industry waste.
10. CRIMSON, Wah & Hua, V8 Environmental, etc.
These are service providers in the general waste, cleaning, and industrial disposal space. While not primarily hazardous-waste specialists, they play important roles in everyday waste logistics and front-line operations.
| Company | Key Strengths / Focus |
| Veolia ES Singapore | Global expertise in hazardous/general waste and energy |
| Sembcorp (SembWaste) | Municipal & industrial solid waste, energy recovery |
| Colex Holdings | Packaging/plastics recycling |
| Recycling Partners | Recycling services across sectors |
| Pride-Chem | Chemical hazardous waste—specialized NEA-licensed streams |
| Tidychem (Tidy Group) | Solvent recycling & distillation (99.4% recovery) |
| Environmental Solutions Asia | Thermal/chemical treatment and precious metal recovery |
| Belfor Singapore | Hazardous waste in post-disaster / industrial cleanup |
| Cramoil Chemical Corp. | In-house chemical waste recycling from chemical processes |
| CRIMSON / Wah & Hua / V8, etc. | General waste logistics and industrial clean-up services |
ECO stands out as the dominant hazardous waste specialist, particularly known for its rotary kiln incinerator, secondary combustion, energy recovery, and integrated wastewater handling for mixed industrial waste streams.
Why Beijing Capital Venture Group Sold ECO? What are the considerations? Financial Market Analysis
On June 18, Beijing Capital Environmental announced that it intends to transfer its 100% stake in ECO Industrial Environmental Engineering Pte Ltd (hereinafter referred to as "Singapore ECO") for a base purchase price of 605.754 million Singapore dollars, equivalent to approximately 3.199 billion RMB. The final buyer is Seche Holdings (SG) Pte. Ltd. In 2015, Beijing Capital Environmental Protection acquired Singapore's ECO for approximately 1.129 billion yuan. Using the base purchase price of 3.199 billion yuan as a simple estimate, ECO's transaction price has increased by approximately 2.07 billion yuan in nine years, a gain of over 180%.
About Beijing Capital Venture Group
At the industry level, the water supply and wastewater treatment industry enjoys strong government support, robust downstream demand, and weak cyclicality. However, the industry is entering a mature stage and faces persistent overcapacity. In particular, China's urban water access rate reached 96.68% in 2010, and the county water access rate increased from 85.15% in 2010 to 97.86% in 2022, with industry capacity utilization at around 60%. The wastewater treatment market has seen annual growth exceeding 5% over the past decade, but urban and county sewage treatment rates reached 98.11% and 96.94%, respectively, at the end of 2022, indicating limited growth potential. Industry fundamentals struggle to sustain continued expansion. Furthermore, due to its extensive involvement in public-private partnerships (PPPs), it faces persistent challenges in collecting payments from private companies, resulting in low overall capital market recognition for the environmental protection industry. Operatingly, water services are the company's core business, accounting for approximately 70% of both revenue and gross profit, followed by solid waste treatment, which contributes approximately 30%.
- The company has 208 sewage treatment projects, with a treatment capacity of 2.727 billion tons in 2022, a national market share of 3.69%, and ranks second among bond issuers. Regional concentration is relatively low, with Shandong, Anhui, and Hunan showing relatively high capacity share.
- The company has 53 water supply projects, primarily located in Anhui (Ma'anshan, Tongling, Huainan), Jiangsu (Xuzhou), Hebei, and Inner Mongolia. In 2022, the company supplied 1.528 billion tons of water, with a market share of 2.27%, ranking fourth among bond issuers.
- Both the sewage treatment and water supply sectors suffer from low capacity utilization. YY estimates that the capacity utilization rates for water supply and sewage treatment (calculated based on daily capacity and annual water supply/sewage treatment volume) are only approximately 51% and 38%, respectively, significantly lower than the company's disclosed capacity utilization rates and those of comparable companies.
- The company's integrated water environment management business is a key focus of its future capital expenditures, primarily under the PPP model. Only since 2021 have some projects entered commercial operation, and a large number of projects are still under construction, resulting in significant uncertainty regarding subsequent payment collection. Furthermore, the major projects currently under construction primarily involve relatively financially weak regions such as Neijiang, Sichuan, Guyuan, Ningxia, and Linli County, Hunan, posing relatively high risks.
- In the solid waste sector, the company operates 65 asset-heavy projects, which is not a leading position in the industry. In 2012, the company realized an investment return of 2.667 billion yuan from the sale of its New Zealand environmental protection company.
Beijing Capital venture group fianancial background:
Financially, the company's earnings performance is relatively solid, but operating profit is relatively weak compared to its peers. Its cash-to-income ratio remained below 0.8 in both 2021 and 2022. Net cash flow from operating activities has declined significantly in recent years and has long been unable to cover cash expenditures from investing activities (except for the significant asset disposal in 2022). Its asset composition primarily consists of various franchises and ongoing PPP projects. Its debt-to-equity ratio has consistently remained above 70%, significantly higher than the industry average. Net cash flow from operating activities/total debt was around 0.05 in both 2021 and 2022, reflecting a heavy long-term debt burden.
However, the company is a leading REIT in the environmental protection industry, having pioneered the issuance of the Fuguo Capital Water REIT, with an offering size of 1.85 billion yuan, achieving a 9.53% appreciation over book value and exploring an exit channel for water projects with long payback periods. Despite the widespread decline in the secondary REIT market since the second half of 2022, Fuguo Capital Water REIT has maintained relatively stable performance, being one of the few products to have remained below its net asset value. The company currently has a clear expansion plan and has received feedback, but progress on the five planned products is significantly behind schedule. Furthermore, the company's first two REIT projects are considered high-quality projects in terms of regional economic and financial strength, capacity utilization, and other factors. However, the asset quality of the remaining projects is weaker than that of the initial batch, making future expansion more difficult.
Beijing Capital Venture Group's acquire of ECO
According to the announcement, in June 2015, Capital Environmental's wholly-owned subsidiary, Capital Hong Kong, signed the "ECO Industrial Environmental Engineering Pte Ltd Share Purchase and Sale Agreement" with Bonland Pte Ltd, proposing to acquire ECO Industrial Environmental Engineering Pte Ltd (hereinafter referred to as the "Target Company," or ECO Singapore) for a total consideration not exceeding S$246 million (approximately RMB 1.129 billion).
At the time, ECO was a leading hazardous waste management company in Singapore. It was the only waste management company in Singapore with sludge treatment capabilities, boasting a 570-ton/day sludge disposal capacity. It was also one of only three companies in Singapore holding a full-service waste collection services license issued by the National Environment Agency (NEA). ECO held a significant market share in Singapore's hazardous waste management sector, with services encompassing hazardous waste incineration, wastewater treatment, solvent recovery, oil recovery, and solidification treatment. Its collection of waste included toxic waste, corrosives, flammable materials, and other hazardous waste generated by industrial companies.
"This acquisition is in line with the company's strategic development," Capital Environmental stated in its 2015 acquisition announcement. It is reported that since 2012, Capital Environmental has been acquiring an increasing number of projects through equity acquisitions, with 2015 being the year the company's overseas asset acquisitions were in full swing. In May 2015, Capital Environmental acquired a 65% stake in New Zealand-based BCG NZ, held by Capital Huaxing, through Capital Hong Kong. BCG NZ's wholly-owned subsidiary, Waste Management NZ Limited, ranks first in New Zealand's waste management industry. In the same year of the acquisition, Capital Environmental's overseas operating revenue increased by 96.91% year-on-year. The company stated that this was primarily due to revenue from newly added subsidiaries in New Zealand and Singapore. The latest financial data shows that in the first quarters of 2023 and 2024, Singapore's ECO company achieved operating revenue of approximately 504 million yuan and 138 million yuan, respectively, and net profits of approximately 117 million yuan and 37.092 million yuan. At the end of the first quarter of 2024, the book value of Singapore's ECO's net assets was RMB 681 million, and the base purchase price for its 100% equity was approximately RMB 3.199 billion.
Why Peking Adventure Group Sold ECO Waste Management Singapore? What is the reason behind?
Strategic Focus on Domestic Environmental Projects
Beijing Capital Environmental Protection announced that the equity transfer of its stake in Singapore’s ECO will effectively reduce asset management risks while enabling the company to concentrate more resources on its core domestic environmental protection projects. The company emphasized that this move aligns with its long-term corporate strategy and supports high-quality development goals. Once the transaction is completed, Beijing Capital Environmental will no longer hold shares in Singapore’s ECO, and ECO will no longer be consolidated into its financial statements.
Optimizing Resources and Financial Impact
The company stated that the divestment will help optimize asset and resource allocation, maximize investment and shareholder returns, and will not cause significant negative impacts on its operations. In fact, it is expected to positively influence operating results in 2024. While the company experienced a performance decline in 2023—with operating revenue of 21.32 billion yuan (down 3.82%) and net profit of 1.606 billion yuan (a 49.09% decrease)—the first quarter of 2024 showed signs of recovery, with net profit reaching 362 million yuan, an 11.89% year-on-year increase. If the transaction progresses smoothly, further benefits are anticipated in the second half of the year.
Strategic Adjustments in Overseas Operations
Industry observers noted that Beijing Capital Environmental has been gradually rebalancing its overseas portfolio. In 2022, the company sold Waste Management NZ Limited, a New Zealand subsidiary it had acquired in 2015, around the same period as its investment in Singapore’s ECO. Analysts interpret these divestments as part of a broader effort to optimize resource allocation and reinforce the company’s domestic market focus. From a capital perspective, Beijing Capital Environmental’s overseas mergers and acquisitions have been financially rewarding, reflecting the success of China’s environmental industry in its global expansion.
Profitable Divestments and Future Outlook
The company’s overseas asset sales have generated significant returns. For example, the divestment of its New Zealand subsidiary produced investment income of approximately NZ$766 million (about RMB 3.021 billion), contributing roughly NZ$551 million (about RMB 2.175 billion) to net profit. At the time, Beijing Capital Environmental stated that China’s domestic environmental protection market has vast potential, and reallocating resources would strengthen its competitiveness in the domestic solid waste sector. Importantly, the company clarified that selling overseas assets does not equate to a complete retreat from international markets; it may still pursue overseas projects closely related to its core business in the future.
What is the realationship between Tialoc and Tongli? Who is the contrator of the Singapore ECO municipal waste treatment incineration plant?

For the Singapore ECO Municipal Waste Treatment Plant, the main contractor is Tialoc, and Tongli provided the OEM manufacturing support by delivering critical heavy machinery used in the plant’s operation. The relationship between Tialoc and Tongli is that Tialoc acts as the EPC contractor and engineering provider, while Tongli serves as the OEM manufacturing base for Tialoc’s projects. Tongli has supplied core process equipment—such as rotary hazarodus incineration kilns, vertical mills, and related systems—for many of Tialoc’s international waste treatment and industrial projects, including the following:
Cleanco UAE
Cleanco Medical Hazardous Waste Incineration Plant Abu Dhabi
The new medical and hazardous waste incinerators in Abu Dhabi and Al Ain are being completed by Tadweer, the Abu Dhabi Waste Management Center. A capacity of 7,500 tonnes of waste per year is provided by the Abu Dhabi facility. The latest incineration technologies are being used at both sites to ensure that waste is collected and treated safely and in an environmentally friendly way. The projects in Abu Dhabi and Al Ain have been reported to have reached 100% completion 5 years ago. Two warehouses and cold storage rooms have been included at each site to store ash and other residues from the incineration process safely. Notice for this project Tialoc is the sub contractor under Tadweer, and TONGLI serves as the OEM manufactuer of Tialoc had provided full sets of the incineration rotary kiln to the client Cleanco waste treatment LLC, Abu Dhabi....
MOBRUK Poland
Mo-bruk S.A. Industrial Hazardous Waste Incineration Plant
On October 11/13/2023, Mo-Bruk representatives led by Karsy Plant Director Mr.Kamil Wójcik visited Tongli for the final factory acceptance test of their hazardous waste incineration rotary kiln. The process included: 1) Reviewing R&D, production, technical parameters and quality control in the exhibition hall; 2) On-site inspection of the kiln’s appearance (welding seams, component installation accuracy) and core performance (drive system speed fluctuation ±0.5% < industry’s ±2%, kiln lining temperature difference <30℃ to ensure 1100-1200℃ incineration); 3) Verifying safety 0.5s response of safety interlock system and environmental protection EU standards. Mr.Kamil Wójcik checked the kiln for meeting contract requirements and exceeding expectations in energy efficiency. Both parties signed the acceptance report, and Tongli arranged packaging, transportation, installation and commissioning to put it into operation at Mo-Bruk’s Karsy Plant afterwards.
Be’ah Oman
In August 25th, 2025 Representatives from the Omani Environmental Services Holding Company (be’ah) visited TONGLI to inspect the manufacturing progress of their 4x15m incineration rotary kiln and the SCC secondary combustion chamber. During the visit, the project manager, Mr. Thomas Ritz Nissen, observed several key stages of production. He witnessed the test run of the friction-drive rotary kiln transmission system, ensuring that the equipment operates smoothly and meets the required performance standards. In addition, he reviewed the welding procedures being applied on critical components and examined part of the NDT (Non-Destructive Testing) documentation, which serves as proof of quality and reliability in line with international standards.
Remondis Polska
Poland Remondis Polska hazardous waste incineration rotary kiln factory acceptance test
Remondis Poland is the Polish subsidiary of the German Remondis Group, one of the world’s largest companies in recycling, water management, and municipal services. Operating in Poland since 1992, the company now runs branches in over 40 cities, offering a wide range of services including municipal and industrial waste collection, recycling, hazardous and medical waste treatment (via Remondis Medison), and e-waste processing (through Remondis Electrorecycling). In recent years, Remondis Poland has also expanded into sustainable energy and district heating with the acquisition of SFW Energia, making it a leading private provider of environmental and utility services supporting Poland’s circular economy.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Question About ECO Waste Management Pte Ltd
ECO Special Waste Management ensures compliance with NEA regulations in multiple ways.
Firstly, it holds full licensing from the NEA as a toxic industrial waste collector, general waste collector, and asbestos removal contractor, indicating it has met the fundamental regulatory requirements to operate in these waste management areas.
Secondly, being certified to ISO 14001 environmental management system, OHSAS 18001, and BizSafe Star level, it has established robust management systems that align with environmental and safety regulations, which are integral to NEA's purview.
Thirdly, its special waste management center equipped with nine treatment and recovery facilities, along with a fleet of over 30 waste collection vehicles and more than 200 ISO tankers, enables it to handle waste in a way that adheres to NEA's waste handling and disposal standards.
Fourthly, the adoption of advanced digital systems in its centralized control room allows for real - time monitoring and control of operations, ensuring any potential non - compliance issues are quickly detected and rectified.
Finally, its SAC - Singlas accredited laboratory, operating to ISO/IEC 17025:2017, accurately analyzes waste characteristics, helping to ensure that all waste treatment and disposal processes meet NEA's strict environmental testing and quality standards.
ECO Special Waste Management adapts to digital transformation in waste treatment through targeted tech integration. It uses advanced digital systems in its centralized control room—paired with sensors and cameras—to remotely monitor and control its nine on-site facilities, enabling real-time operational adjustments. The company also leverages AI and IoT: AI analyzes video footage to predict equipment issues and optimize waste flow, while an AI-powered IoT system tracks plant performance, sets operation times, and triggers alarms for anomalies. Additionally, it integrates office automation (with a mobile-friendly interface for on-the-go worker input) with existing ERP and SCADA systems, creating a seamless, data-driven workflow that cuts manual effort and boosts decision-making efficiency.
Under Séché Environnement, ECO Special Waste Management is set to embark on a transformative journey. Séché Environnement, a leading force in waste treatment and recovery globally with a presence in 15 countries and over 120 sites, brings a wealth of expertise. It has a strong focus on the circular economy, which will likely be integrated into ECO's operations. This could mean enhanced waste - to - energy initiatives. For instance, ECO may start to convert more of the waste it collects into electricity, steam, or hot water, following Séché's model of reducing the carbon footprint of industrial, tertiary, and residential consumption.
Séché's R & D - developed advanced technologies such as thermal, physico - chemical, or biological treatments could be transferred to ECO. This would enable ECO to handle waste more efficiently, especially complex and hazardous waste, expanding its service capabilities. ECO may also benefit from Séché's experience in decontamination and rehabilitation activities, which could lead to new business opportunities in Singapore, like cleaning up polluted industrial sites.
Furthermore, Séché's commitment to regulatory compliance, as evidenced by its efforts in France to meet anti - corruption and other regulations, will likely rub off on ECO. ECO will likely strengthen its own compliance programs, ensuring it continues to meet and exceed Singapore's NEA regulations. With Séché's global reach, ECO may also explore international expansion in the future, tapping into new markets and sharing its waste management knowledge on a broader scale.
ECO Special Waste Management uses targeted technologies to boost safety. It leverages AI-powered video analysis and sensors (integrated with its centralized control system) to monitor operations—detecting hazards like improper waste handling or equipment anomalies in real time and triggering timely interventions. The company also uses ISO-certified waste transport vehicles with built-in safety tracking (to ensure secure waste movement) and an AI-driven IoT system that alerts teams to abnormal equipment performance, preventing breakdowns that could pose risks. Additionally, its SAC-accredited, ISO/IEC 17025-compliant laboratory uses precise analytical tech to identify waste characteristics, ensuring only safe, regulated treatment methods are used, while mobile-friendly digital tools let on-site workers access safety protocols and report issues instantly.
Based on over 25 anonymous employee reviews on Glassdoor, the company received an overall rating of 2.7 out of 5. 30% of employees would recommend the company to a friend, and 46% expressed a positive outlook on the company's prospects.
On the positive side, employees mentioned the company's good benefits, friendly coworkers, and opportunities for career development. The company prioritizes safety, and its use of advanced digital systems, such as real-time AIoT, not only improves work efficiency but also enhances workplace safety, a crucial safeguard for employees.
However, the company also has some shortcomings. Employees generally report that the company's culture and values score low, at just 2.2, and management needs improvement. Work-life balance also received a score of 2.2, suggesting employees may experience high levels of work pressure. Furthermore, compensation is perceived as uncompetitive, which may impact employee job satisfaction.
ECO Special Waste Management holds several important certifications and licenses. It is fully licensed by the National Environment Agency (NEA) as a toxic industrial waste collector, general waste collector, and asbestos removal contractor.
Additionally, it is certified to the ISO 14001 environmental management system, OHSAS 18001 (now ISO 45001) occupational health and safety management system, and has achieved BizSafe Star level. The company's special waste management center is equipped with facilities that meet regulatory requirements.
Moreover, its laboratory is accredited by SAC - Singlas to ISO/IEC 17025:2017, which is crucial for accurate waste analysis. It also possesses other certifications such as the ISO 9001 quality management system certification, and relevant licenses like the road transportation license for its waste collection vehicles.
Conclusion:
ECO Special Waste Management Pte Ltd’s hazardous waste incineration plant is more than a disposal facility; it is a cornerstone of Singapore’s waste ecosystem. In a country where land is scarce and regulations are among the strictest in the world, the plant provides a safe, reliable, and compliant solution for treating toxic and industrial waste that cannot be managed through conventional means. By combining advanced incineration technology with strict adherence to environmental standards, ECO supports Singapore’s goals of protecting public health, reducing landfill dependency, and advancing toward a sustainable circular economy. Its role is therefore not only operational, but strategic-ensuring that hazardous waste is neutralized responsibly while contributing to the nation’s long-term vision of resilience and sustainability. So, above is the introduction. At the same time, Tongli Heavy Machinery also offers solutions beyond waste incineration rotary kilns. We manufacture vertical roller mills, ball mills, and fertilizer production lines. If you are interested in our other products, please feel free to contact us.

















