
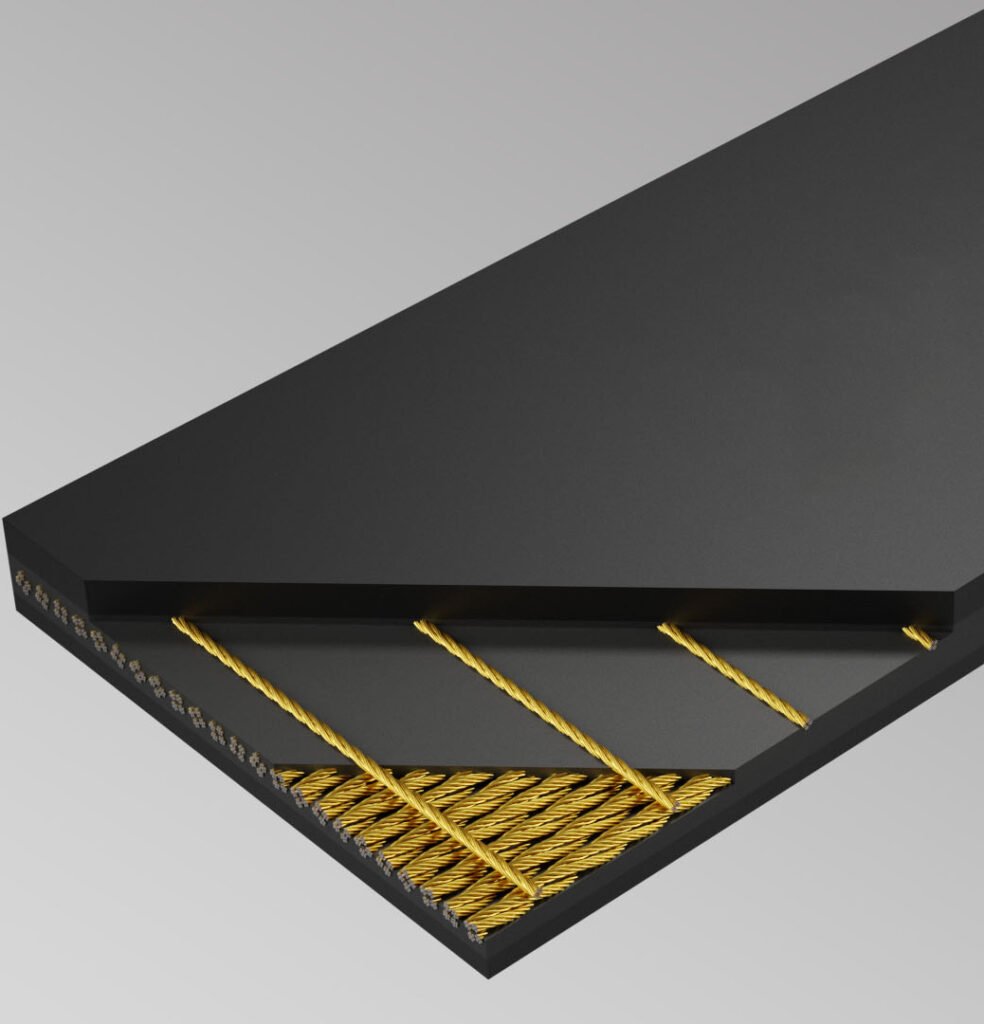
Steel cord conveyor belts, also known as steel cord belts, are high-strength rubber steel cord belts constructed from longitudinally arranged steel cords covered with a special rubber covering. This type of steel-cord conveyor belting is designed for long-distance steel cord belt applications, handling heavy-duty steel cord belt conveying needs in material conveying systems. A steel cord rubber conveyor belt or steel wire rope core conveyor belt is widely used in industries such as coal, mining, ports, metallurgy, power generation, and chemicals, where industrial steel cord conveyor belts are critical for large-scale transportation. Their unique structure provides high tensile steel cord conveyor belt performance with exceptional tensile strength and durability, making them a key solution in steel reinforced conveyor belt applications. These belts deliver excellent impact resistance and abrasion resistance, resulting in superior strength, low elongation, and outstanding flexural fatigue resistance. Each steel cord is encased in special insulating rubber to reduce internal friction and enhance adhesion, ensuring reliable bonding within the steel cord belting. The upper and lower rubber coverings are specifically designed based on application requirements, with various ST steel cord conveyor belt types and specifications available to provide maximum protection for the steel cords. Whether handling standard bulk materials or highly abrasive loads, a steel cable conveyor belt ensures long service life and reliable operation.Thanks to the high strength of the steel cords, these belts allow extremely short take-up travel, smaller drive pulleys, and more compact equipment design. A long distance steel cord belt is particularly suitable for working conditions with high pulling force, large transport capacity, and high-speed operation. It can also stably transport materials at large inclination angles while maintaining excellent durability and reliability in harsh environments and high-intensity operations.
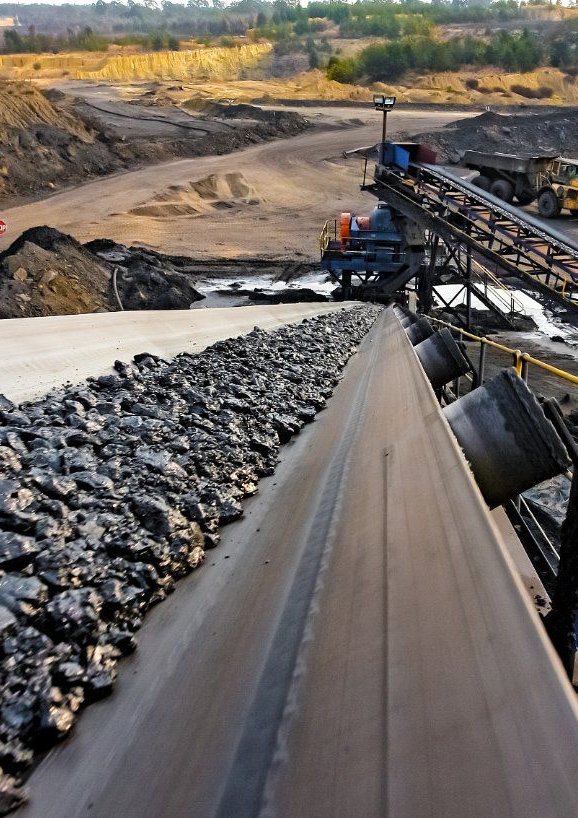

Steel Cord Conveyor Rubber Belt Manufacturer
A MACHINE YOU CAN DEPEND ON!
Understand the advantages of steel cable conveyor belt solutions offering high tensile strength, minimal elongation, and excellent load-bearing capacity.
The specially treated galvanized or brass-plated high carbon steel wire rope has extremely high tensile strength and fatigue resistance. The wire ropes are arranged in parallel with precise spacing, providing the core load-bearing capacity for the conveyor belt.
The surface of the steel wire rope is galvanized, and the rubber used has good adhesion to the steel wire rope, so that the rubber and the steel wire rope are tightly bonded, impact-resistant, and not easy to fall off, thereby extending the service life of the tape.
Using an advanced constant-tension forming process, the wire ropes are evenly arranged and have consistent tension, ensuring balanced tape operation and preventing deviation . Rigorous online non-destructive testing ensures that each wire rope's spacing, arrangement, and rubber penetration meet the highest standards, eliminating internal defects.
| Strength level | tensile strength(N/mm²) | Wire rope pitch (mm) | Wire rope diameter (mm) | Minimum breaking force (kN) | Minimum covering thickness (mm) |
| ST-500 | 500 | 10 | 2.5 | 5.5 | 4 |
| ST-630 | 630 | 10 | 2.8 | 7 | 4 |
| ST-800 | 800 | 10 | 3 | 8.9 | 4 |
| ST-1000 | 1000 | 12 | 3.4 | 12.9 | 4 |
| ST-1250 | 1250 | 12 | 3.8 | 16.1 | 4 |
| ST-1400 | 1400 | 12 | 4.3 | 18 | 4 |
| ST-1600 | 1600 | 12 | 4.7 | 20.6 | 4 |
| ST-2000 | 2000 | 12 | 5 | 25.6 | 4 |
| ST-2250 | 2250 | 12 | 6.6 | 29 | 4 |
| ST-2500 | 2500 | 15 | 6.8 | 40 | 5 |
| ST-2800 | 2800 | 15 | 7 | 44.8 | 5 |
| ST-3150 | 3150 | 15 | 7.3 | 50.5 | 5.5 |
| ST-3500 | 3500 | 15 | 8.2 | 56 | 6 |
| ST-4000 | 4000 | 15 | 8.8 | 63.5 | 6.5 |
| ST-4500 | 4500 | 16 | 9.7 | 76.3 | 7 |
| ST-5000 | 5000 | 17 | 10.9 | 91 | 7.5 |
| ST-5400 | 5400 | 17 | 11.3 | 98.2 | 8 |
The primary difference lies in the frame material and structure. ST belts use steel wire rope as a longitudinal frame, offering extremely high tensile strength and very low elongation, making them suitable for long-distance, high-volume, and heavy-load transport. EP/NN belts, on the other hand, use polyester (EP) or nylon (NN) fabric as a frame. This material offers relatively low strength and high elongation, but is lighter and more flexible, making them suitable for short to medium distances and smaller transport volumes. The choice depends on the specific transport distance, transport volume, tension, and cost budget.
Key factors include:
Material characteristics: Sharp and abrasive materials will accelerate the wear of the cover rubber.
Conveyor system condition: Whether the rollers are aligned, whether the rollers are slipping, whether the cleaners are effective, etc. will directly affect the wear and damage of the belt.
Joint quality: The process quality of the vulcanized joint is the weakest link of the conveyor belt. Failure of the joint will cause the entire belt to be scrapped.
Environmental factors: Exposure to UV rays, ozone, oils or extreme temperatures will accelerate rubber aging.
Maintenance: Regular inspection, timely repair and correct tensioning maintenance are essential.
Steel cord conveyor belts must use hot vulcanized joints. This process includes several key steps:
1.Separate the two ends of the belt to expose the steel wire rope;
2.Step cutting and grinding of wire rope;
3.Use special core and surface adhesives to stagger and butt the wire ropes at both ends;
4.Use a dedicated vulcanizing machine to heat and pressurize the joint at a specific temperature, pressure, and time to vulcanize the rubber and wire rope into a solid whole. This is a highly technical process and must be performed by professionals.
"ST" stands for "Strength," and the number following it (e.g., ST1000) represents the rated tensile force (in kilonewtons) per millimeter of belt width. For example, a 1000mm wide conveyor belt rated ST1000 has an overall rated tensile strength of 1000 kN/m * 1 m = 1000 kN. The choice of ST grade is determined by professional designers based on the maximum operating tension calculated based on parameters such as the conveyor's total length, lift height, belt speed, and conveying capacity.
The selection needs to be based on detailed engineering calculations, with key considerations including:
Conveying capacity: the number of tons of material that needs to be transported per hour.
Conveying distance and lifting height: determine the required belt tension.
Material properties: density, particle size, abrasiveness, humidity, temperature, etc.
Working environment: indoor/outdoor, temperature, corrosiveness, etc.
1.Galvanized Steel Wire Rope: The wire rope is composed of multiple filaments, offering high flexibility and low elongation, enabling efficient, high-strength splicing designs. The galvanized coating forms a bond between the wire rope and the insulation, creating a valuable corrosion barrier.
2.Insulation Rubber (Core Rubber): Leveraging our extensive rubber compounding expertise, we have developed a superior insulating adhesive rubber that penetrates and adheres to the wire rope. This results in excellent adhesion, corrosion resistance, and splicing efficiency.
3.Top Cap Breaker: Provides additional localized puncture resistance, preventing heavy impact loads from causing premature carcass failure.
4.Bottom Cap Breaker: Provides additional localized puncture resistance, preventing trapped material from causing premature carcass failure.
5.Outer Rubber Cover: The top and bottom of the jacket utilize advanced composite materials designed to protect the wire rope's strength members from the harsh environmental conditions common in most conveying applications. These composite materials can withstand abrasion, saw-tooth cutting and gouging, high impact, subzero temperatures, moderately high temperatures, the hardening effects of ozone attack, and flame spread.
1.Galvanized High-Tension Open-End Steel Cord
These steel cords offer high flexibility, low elongation, and an efficient, high-strength splice design. The galvanized coating acts as a bond between the steel cord and the rubber, creating a critical corrosion barrier.
2.Limited Travel
Tongli conveyor belts have a maximum elongation of 0.25% at rated tension. This enables the use of lower-cost tensioning systems in many applications, making them the preferred choice for long-haul land transport and short-haul stockpiling/reclaim systems where minimum elongation is critical.
3.Long Splice Life:
Our proven splicing method, verified by a dynamic splice tester, achieves dynamic splice efficiencies exceeding the 50% rating defined in DIN 22131 Part 3. With proper technique, splices on your belt should extend the life of the belt.
4.High Impact Resistance
The combination of an advanced cover compound and skim rubber with excellent adhesion provides the impact, tear, and rip resistance your application requires.
5. Reduced Cost Per Ton
Fewer conveyors and connectors, faster take-up times, and reduced belt inventory extend belt and connector life and reduce downtime. All of these factors contribute to a lower cost per ton of material conveyed, significantly improving your profitability.
The tensile strength of common steel cord conveyor belt models is as follows:
ST630: 630 N/mm
ST800: 800 N/mm
ST1000: 1000 N/mm
ST1250: 1250 N/mm
ST1600: 1600 N/mm
ST2000: 2000 N/mm
ST2500: 2500 N/mm
ST3150: 3150 N/mm
ST3500: 3500 N/mm
ST4000: 4000 N/mm
ST4500: 4500 N/mm
ST5000: 5000 N/mm
ST5400: 5400 N/mm
The Tongli brand ST steel cord conveyor belt (model ST4000) has performed exceptionally well in the main coal transportation system of a large open-pit coal mine. As a type of steel cord conveyor belt, it is engineered to handle an average daily transport volume of 45,000 tons under extreme working conditions. The heavy duty steel cord belt must withstand heavy loads, with a maximum single coal stream weight of 1,200 kg/m, continuous operation for over 20 hours a day, and long-term exposure to harsh winds, sandstorms, and temperature swings of up to 15°C between day and night. Thanks to its 8+4-layer, highly wear-resistant natural rubber cover (wear loss ≤ 120 mm³), galvanized high-strength steel cord belt core (breaking strength ≥ 4,000 N/mm), and tear-resistant edge reinforcement, the Tongli steel-cord conveyor belting has been running stably at the mine for six years. During this period, it has transported over 98 million tons of coal with only three routine vulcanization repairs and no core structural damage. Compared to other steel wire rope core conveyor belt products previously used at the site, the Tongli steel cord rubber conveyor belt boasts a 25% longer service life, making it a reliable and cost-effective solution for heavy-load, high-frequency, and environmentally resistant coal mine operations.
Conventional smooth steel cord conveyor belts are typically suitable for conveying bulk materials at inclination angles of no more than 16°–20°. When a patterned overlay is applied to improve material adhesion, the inclination angle can be increased to 25°–30°. The belt strength must be carefully matched to the operating conditions. For example, the ST4000 high tensile steel cord conveyor belt (breaking strength 4000 N/mm) can withstand the tensile loads encountered at steep angles. For extremely steep angles exceeding 30°, a steel reinforced conveyor belt with corrugated sidewalls and T-shaped cross-partitions is required, enabling vertical conveyance at inclination angles up to 90°. With this design, the maximum material size is 400 mm, and conveying capacity can reach 6000 m³/h. Tongli’s engineering projects demonstrate that combining a concave-cored steel cord belting with a double-row V-shaped roller trough allows stable coal transportation at a 28.5° incline. In one project, a coal mine using STJ800 equipment successfully achieved the heavy-duty task of transporting 900,000 tons annually at a 23° inclination. For such demanding applications, heavy duty steel cord belts, industrial steel cord conveyor belts, or even rubber steel cord belts are preferred for their durability and wear resistance. In long-haul projects, the use of long distance steel cord belts or steel cable conveyor belts ensures reliable, energy-efficient performance. Frequency conversion soft starting is also crucial to control tension fluctuations, while a safety factor of ≥7 is required for safe and reliable operation.
ST rubber belts typically covers width range of 200mm-2400mm to accommodate varying conveying capacity requirements. Small belt conveyors often use narrow belts ranging from 200mm to 600mm, while open-pit mine main transport systems often utilize wide belts ranging from 1000mm to 2000mm. Some large ports even use ultra-wide belts of 2450mm. The width selection is highly compatible with the belt. For example, the ST4000 belt has a minimum width of 1000mm, corresponding to 64 wire ropes. Thickness is determined by the wire rope diameter and the thickness of the cover rubber, typically ranging from 16mm to 30mm. For example, the ST630 uses a 3mm diameter wire rope with 5mm of cover rubber on each end, for a total thickness of approximately 13mm (including the core rubber). The ST5400 uses an 11.3mm diameter wire rope with 9mm of cover rubber on each end, for a total thickness of 29.3mm. The cover rubber thickness can be customized, increasing to 10mm for wear-resistant conditions and reducing to 4-6mm for high-temperature environments. Special types, such as tubular belts, can be up to 3100mm wide, corresponding to a pipe diameter of 850mm. The thickness increases in tandem with the pipe diameter, meeting the needs of enclosed and heavy-load conveying.
Our steel wire rope core conveyor belt, designed as part of Tongli’s advanced steel cord conveyor belt series, utilizes multi-layer structural protection, optimized materials, and enhanced processes to ensure high strength, corrosion resistance, and impact protection. First, the wire rope is treated with corrosion protection, where the surface is coated with zinc or aluminum. A thick zinc coating of 15–30 μm provides sacrificial anodic protection in corrosive environments with moisture or sulfur, offering more than three times the corrosion resistance of ordinary smooth steel rope. For extreme conditions, nylon- or plastic-coated ropes are also applied to further isolate the steel cord belt from chemical agents.
Next, the wire rope is embedded in a specialized core rubber with a Shore hardness of 60–70. This core rubber creates a cross-linked bond with the wire rope coating, achieving a 100% gap-filling rate to prevent moisture and material debris infiltration. The outer layer is reinforced with a 4–10 mm thick wear-resistant cover (such as neoprene) to endure material impact and abrasion, with a wear loss of ≤120 mm³. Additional reinforcement, such as a polyester canvas interlayer between the cords, increases belt stability. At the joints, hot-vulcanized adhesive ensures seamless bonding between the core rubber, surface rubber, and the body, with bonding strength not less than 90% of the original belt body, preventing exposure or damage to the cords.
This robust structural design makes Tongli’s steel-cord conveyor belting and steel cord rubber conveyor belt ideal for heavy-duty use in mining and bulk handling. In applications requiring high breaking strength, such as the ST steel cord conveyor belt, the system demonstrates long service life and exceptional reliability. Compared to conventional designs, this heavy duty steel cord belt provides superior protection and consistent performance even in the harshest environments.
Grade H (Severe Cutting and Tearing): Tensile strength ≥ 24 MPa, elongation at break ≥ 450%, abrasion loss ≤ 120 mm³. Suitable for conveying sharp, abrasive materials that can severely damage the conveyor belt, such as unprocessed metal ore, limestone, and granite.
Grade D (Severe Abrasion): Tensile strength ≥ 18 MPa, elongation at break ≥ 400%, abrasion loss ≤ 100 mm³. Suitable for conveying highly abrasive materials such as sand (with sharp edges).
Grade L (Moderate Abrasion): Tensile strength ≥ 15 MPa, elongation at break ≥ 350%, abrasion loss ≤ 200 mm³. Suitable for conveying moderately abrasive materials such as rubber and coal (surface layers), as well as dry materials with minimal or no abrasion, such as smooth sand and ground cement.
X-Grade: Tensile strength ≥25MPa, elongation at break ≥450%, abrasion resistance ≤120mm³. Featuring a heavy-duty cover, it offers excellent impact and cut resistance, making it suitable for conveying large, sharp materials (such as iron ore and granite).
W-Grade: Tensile strength ≥18MPa, elongation at break ≥400%, abrasion resistance ≤90mm³. It offers excellent erosion and wear resistance, specifically designed for conveying small, highly abrasive materials (such as quartz sand and fine gravel).
K-Grade: Tensile strength ≥20MPa, elongation at break ≥400%, abrasion resistance ≤200mm³. It is flame-retardant and suitable for use in flammable and explosive environments such as underground coal mines and chemical plants where fire protection is required.
VT Grade: Tensile strength ≥17MPa, elongation at break ≥350%, abrasion resistance ≤175mm³. Also flame-retardant, it offers excellent low-temperature adaptability and can operate stably in environments ranging from -15°C to 40°C.
T120 Grade: Tensile strength ≥15MPa, elongation at break ≥400%, abrasion resistance ≤175mm³. It offers heat resistance and can withstand material temperatures up to 120°C, making it suitable for conveying high-temperature materials such as sintered ore and hot slag.
The maximum load-bearing capacity of a steel cord conveyor belt depends on a combination of belt strength grade, belt width, and belt speed. However, this is primarily determined by the tensile strength and structural design of the steel cord core, which can vary significantly under different operating conditions. From a basic load-bearing perspective, belt strength directly determines its tensile load capacity. Conventional models ST630 to ST5400 have rated tensile strengths of 630-5400 N/mm, while high-end models like the ST10000 have surpassed 10,000 N/mm, with a single wire rope breaking force of up to 152 kN. Actual throughput is closely related to belt width and speed. For example, the ST4500, with a 2400mm width and a belt speed of 4.0 m/s, can achieve a maximum throughput of 15,062 m/h when conveying ore with a bulk density of 2.5 t/m³. In extreme heavy-load applications, the TONGLI ST7800 achieved a transport capacity of 11,000 tons/hour at Tibet Julong Copper Industry, while the ST6300 can transport 10,000 tons of material over a height difference of 566 meters. It is important to maintain a safety factor between 7 and 9 to avoid structural damage caused by overload.
The ST1000 has a rated tensile strength of 1000 N/mm and commonly uses φ3-4 mm steel wire rope with a total belt thickness of 16-18 mm. It is suitable for small and medium-sized conveying systems, such as small mines and power plant coal transportation lines, and can meet conditions with conveying distances ≤ 500 meters and single coal flow weights ≤ 600 kg/m. The ST2000 has a rated tensile strength of 2000 N/mm and uses φ6-7 mm steel wire rope with a belt thickness of 20-22 mm. It is suitable for medium-sized systems such as medium-sized coal mines and bulk cargo transportation at ports, and can handle distances of 500-1500 meters and coal flow weights ≤ 1000 kg/m. The ST3150 has a rated tensile strength of 3150 N/mm and uses φ8-9 mm steel wire rope with a belt thickness of 24-26 mm. It is mainly used in large and long-distance applications, such as open-pit mine main transportation lines, and can carry distances greater than 1500 meters. m, and coal flow weight ≤1400kg/m. Higher grades, such as ST4500 (4500N/mm) and ST5400 (5400N/mm), have wire rope diameters of up to φ10-11.3mm and belt thicknesses of 28-30mm. They are suitable for ultra-large projects, such as long-distance cross-regional transportation. The safety factor is typically 7-9, and the higher the grade, the closer the safety factor is to the upper limit to prevent structural damage caused by tension overload.
For impact resistance, the belt body utilizes a "high-elastic core rubber + buffer transition layer" design. The core rubber is made of natural rubber with a Shore hardness of 55-60 and an impact absorption capacity of ≥15kJ/m², capable of cushioning the impact of falling large materials (such as 500kg ore). The buffer transition layer, 3-5mm thick, distributes local stress and protects the wire rope from direct impact damage. For example, the ST3150 belt, when subjected to the impact of a 1.5m drop, achieved a deformation recovery rate of over 90%, with no core layer cracking. Wear resistance is achieved through the use of a highly abrasion-resistant cover rubber. Conventional D-grade cover rubber has an abrasion loss of ≤100mm³ (DIN standard), while the special W-grade version has an even lower abrasion loss of ≤90mm³. The cover rubber also incorporates additives such as carbon black and vulcanizers to enhance tear strength (≥35kN/m). Furthermore, the wire rope spacing is controlled at 8-12mm, and combined with the 6-10mm thick upper and lower rubber covers, a stable support structure is formed, reducing localized wear caused by material friction. In our experience, this design extends the conveyor belt's service life by over 30% compared to conventional belts when conveying highly abrasive materials such as quartz sand.
The elongation of steel cord conveyor belts under load is divided into elastic elongation and permanent elongation. The elastic elongation is primarily influenced by the belt's strength grade, the characteristics of the wire rope, and the load tension, and is governed by clear industry standards. Elastic elongation is a reversible deformation that recovers with the removal of the load. The standard ST series belts exhibit a stable elastic elongation of 0.3%-0.5% at rated tension. For example, the ST1000 belt exhibits an elastic elongation of approximately 0.3-0.5 meters per 100 meters of belt at a rated tension of 1000 N/mm. The ST3150 belt exhibits a slightly lower elastic elongation of approximately 0.25%-0.4% due to its larger wire rope diameter (φ8-9mm) and higher strength. Permanent elongation is an irreversible deformation caused by the plastic deformation of the wire rope and must be strictly controlled to a low range. When a new belt is first used, the permanent elongation is typically ≤0.2% under a pretension of 10%-15% of the rated tension. After long-term operation, the cumulative permanent elongation must be ≤0.5%, otherwise it will affect the conveyor belt's centering. A "pre-tensioning process" is used to control elongation during construction. For example, when the ST2000 belt is used on a 1000-meter conveyor line, it requires a pre-tension of 1.5-2 meters during installation (including elasticity and initial permanent elongation). During operation, the tensioning device dynamically adjusts the belt's elongation to within the designed threshold to prevent slippage and joint cracking.
There are three main methods for splicing steel cord conveyor belts: mechanical splices, cold-bonded splices, and hot-vulcanized splices.
Mechanical splices are an emergency or temporary solution, connecting with metal fasteners. They require no specialized equipment and can be completed in less than 10 minutes. However, the splice strength is only 50%-60% of the original belt, and the fasteners can easily cause stress concentration. Therefore, they are only suitable for temporary conveying scenarios with low belt strengths (ST1000 or less) and low speeds (≤1.6m/s), such as emergency repairs in small mines, or for fertilizer production line belts, where conveyor belts bear little load. This type of belt fastener can be considered for labor-saving applications. In our African fertilizer project, where on-site resources are limited, using this type of belt fastener can save installation time.
Cold-bonded splices are bonded using a specialized adhesive. The overlap length should be determined by "1-1.2 times the belt width" (e.g., 1050-1200mm for a 1000mm wide belt). The curing time is ≥4 hours. The joint strength can reach 70%-80% of the original tape, eliminating the need for high-temperature equipment. It's suitable for underground applications where hot vulcanization isn't feasible. However, it requires extremely high ambient humidity (≤70%) and adhesive quality.
Hot vulcanization is the optimal joint method I would say, requiring precise control of the three key elements: temperature, pressure, and time: a temperature of 145±5°C, a pressure of 1.4±0.2MPa, and a time calculated as "tape thickness x 2 + 10 minutes" (e.g., 50 minutes for a 20mm thick tape). The overlap length increases with tape strength, ranging from 300-500mm for the ST630 model and 800-1200mm for the ST3150 model. The joint strength can exceed 85% of the original tape, making it suitable for long-distance, high-volume systems.
1. Regularly inspect cover rubber wear: Use a depth gauge to check the thickness of the upper and lower cover rubber weekly. If wear reaches 1/3 of its original thickness (e.g., 3mm remaining from a 9mm layer) or if there is partial core exposure, repairs are required. Using the DIN abrasion test, if wear exceeds 150mm³/1.61km, replacement is necessary to prevent direct wear of the wire rope from the material.
2. Monitor conveyor belt tension: Measure belt elongation monthly. If elastic elongation exceeds 0.5% or permanent elongation exceeds 0.2%, adjustment is required using the tensioning device. For high-strength conveyor belts of ST3150 and above, tension should be controlled within 15%-20% of the rated tensile strength (e.g., for ST3150 belts, the tension per meter is ≤630N/mm) to prevent overtightening that could damage the core.
3. Check joint condition: Inspect vulcanized joints quarterly and use an ultrasonic detector to detect internal bubbles or debonding. If joint strength drops by more than 10% of the original belt (e.g., strength drops from 85% to 75%), re-vulcanize. Mechanical joints should be inspected for loose fasteners and torque maintained at 25-30 N·m to prevent joint slippage.
4. Clean rollers and pulleys: Clean adhesive from roller surfaces every two weeks to ensure radial runout is ≤0.5mm and rotational resistance is ≤3N. Replace pulley covers if wear exceeds 5mm to prevent belt deviation (deviation should be within 5% of the belt width) and reduce edge wear.
5. Control material impact: Install impact pads at material drop points. The compression of the impact pads should be ≤20mm (when supporting a 500kg material impact) to prevent material drops exceeding 3m from directly impacting the belt. Material with a particle size greater than 300mm should be crushed first to prevent tearing of the cover rubber.
6. Environmental Protection and Anti-corrosion: In humid or corrosive environments (such as chemical plants and coastal ports), apply rust inhibitor to the conveyor belt edges and joints monthly. In flame-retardant environments, such as underground, the belt's flame retardancy should be tested every six months. The oxygen index must be ≥30% to ensure compliance with GB 10822.
7. Record and Alert Management: Maintain a maintenance log to record daily operating hours (single shift operation should not exceed 12 hours to avoid fatigue damage) and conveying volume (not exceeding 110% of the design value). If the average daily wear of the cover rubber exceeds 0.1mm or the joint temperature exceeds 60°C, an alert will be triggered and the machine will be shut down for maintenance.
From a repair perspective, for local surface damage to conveyor belting rubber, such as minor cover rubber scratches or small exposed core areas without damage to the steel wire rope, cold adhesive repair can be applied. First, grind the damaged area with an angle grinder to create a rough surface, then apply a specialized adhesive with high shear strength. Press and bond a patch of matching rubber conveyor belt material under uniform pressure. After curing, the belt can be put back into service, with wear resistance restored to over 90 percent of the original steel cord conveyor belt.
For minor vulcanized splice delamination, local heating vulcanization can restore the joint, maintaining strength above 80 percent of the original industrial steel cord conveyor belt.
However, when damage reaches the core structure or critical limits, replacement is necessary. Steel wire breakage occurs when individual wires snap or multiple wires break along the belt length, reducing the high tensile steel cord conveyor belt strength and risking overall tearing. Large-area cover rubber damage or transverse belt tears compromise sealing and load distribution, making repairs ineffective. Permanent elongation beyond safe limits or aging of the core rubber can reduce stability of the heavy duty steel cord belt, rubber steel cord belt, steel cord rubber conveyor belt, and other steel cord belting, causing slippage, misalignment, and safety hazards.
Following these repair and replacement guidelines ensures reliable performance and long service life of long distance steel cord belts, steel cable conveyor belts, and other steel reinforced conveyor belts in mining, bulk material handling, and industrial applications.
Flame Retardant Properties
These steel cord conveyor belts and rubber steel cord belts use flame-retardant rubber such as chloroprene or brominated butyl for both the cover and core. Flame retardant additives like aluminum hydroxide and decabromodiphenyl ether are incorporated, achieving an oxygen index of 30 percent or higher in compliance with coal mine flame-retardant standards. The belts self-extinguish within ten seconds when exposed to an open flame for thirty seconds at 1000 degrees Celsius, with no molten droplet formation. This makes them safe for use in flammable and explosive environments such as underground coal mines and chemical plants, preventing fires caused by material friction or electrical faults.
Tear-Resistant Design
The belt body is reinforced with longitudinal polyester canvas layers to achieve a tear strength of 35 kilonewtons per meter. High-strength steel cords are densely arranged with spacing reduced to eight millimeters or less in models ST3150 and above, forming a tear-resistant network that limits puncture damage from sharp materials such as ore fragments to a range of 50 millimeters and prevents overall belt rupture. Some premium models include aramid anti-tear strips at the edges to further enhance tear resistance.
Anti-Tracking and Anti-Slip Structure
The belt edges feature a wedge-shaped design combined with alignment rollers in the conveyor system to keep misalignment within five percent of the belt width. The cover rubber surface is pressed with diamond or herringbone patterns with a depth of three to five millimeters, achieving a friction coefficient of 0.45 or higher. This prevents material slippage in inclines up to 25 degrees and is ideal for coal, wet clay, and other slippery materials.
High and Low Temperature Protection
Special models such as T120 use heat-resistant rubber to handle materials at temperatures up to 120 degrees Celsius, such as sintered ore. The belts maintain elasticity in low temperatures down to minus thirty degrees Celsius with modulus variation under fifteen percent, avoiding cracking. These properties make them suitable for outdoor winter mining in northern regions or high-temperature material handling in steel mills.
The unit price per meter of a steel cord conveyor belt depends on tensile strength, belt width, performance requirements, and purchase volume. Different parameter combinations result in significant price variations.
For example, a basic ST630 model with rated tensile strength of 630 N/mm and a belt width of 1200 millimeters, covered with six millimeters of top and bottom rubber, is priced between four point five and nine point five US dollars per meter for minimum orders of thirty meters.
A medium-strength ST1250 model with a 1000-millimeter width and a belt mass of 21.6 kilograms per meter costs approximately seven point five US dollars per meter for purchase quantities of fifty to ninety-nine meters, with prices dropping to seven point four dollars per meter for orders exceeding one hundred meters.
High-strength ST2000 models with rated tensile strength of 2000 N/mm and a 1400-millimeter width with eight-millimeter cover rubber can range from twenty to one hundred thirty dollars per meter, with a minimum order of one hundred meters.
Special performance rubber steel cord belts command higher prices. Flame-retardant models meeting DIN K ST standards for underground mining applications with 1200-millimeter width and ST1000 strength level are typically priced between thirty and thirty-five dollars per meter. High-temperature T120 models capable of handling materials at 120 degrees Celsius with ST1600 strength and a 1000-millimeter width range from twenty-five to one hundred dollars per meter, with prices increasing alongside cover rubber thickness between six and ten millimeters.
Belt width also strongly affects pricing. Conventional models with 800-millimeter width cost around four to six dollars per meter, whereas 1200-millimeter width belts rise to thirty-nine to fifty-eight dollars per meter. Extra-wide belts of 1600 millimeters and above, such as ST3150 models, can exceed one hundred fifty dollars per meter and must be custom manufactured according to project requirements, with production timelines and costs increasing accordingly.
This pricing overview applies to steel cord rubber conveyor belts, industrial steel cord conveyor belts, heavy duty steel cord belts, and steel cord belting used in mining, bulk material handling, and heavy industrial applications.
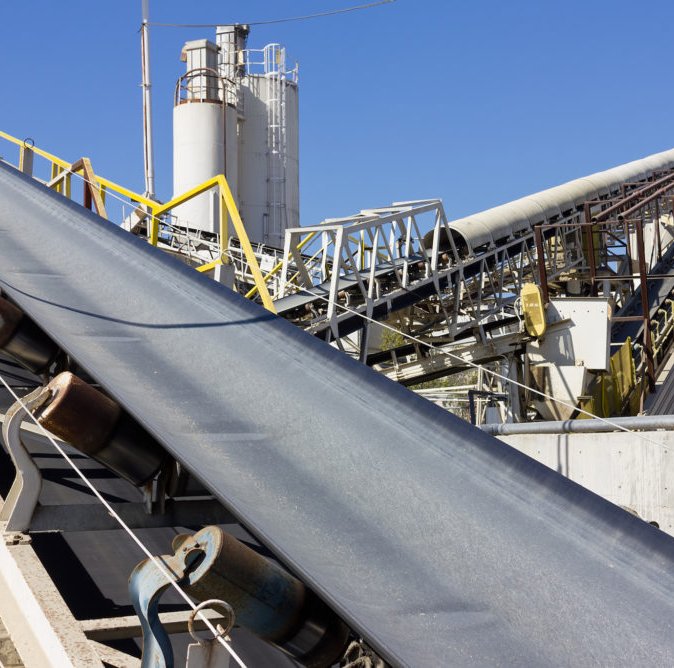

From limestone crushing to clinker burning, in the entire process chain of cement production, steel cord conveyor belts are responsible for transporting various raw materials, mixed materials and finished cement.

In large open-pit coal mines or metal mines, large amounts of ore and stripping materials need to be transported continuously for several kilometers or even dozens of kilometers. Steel cord belts can achieve long-distance and large-volume transportation with a single machine.
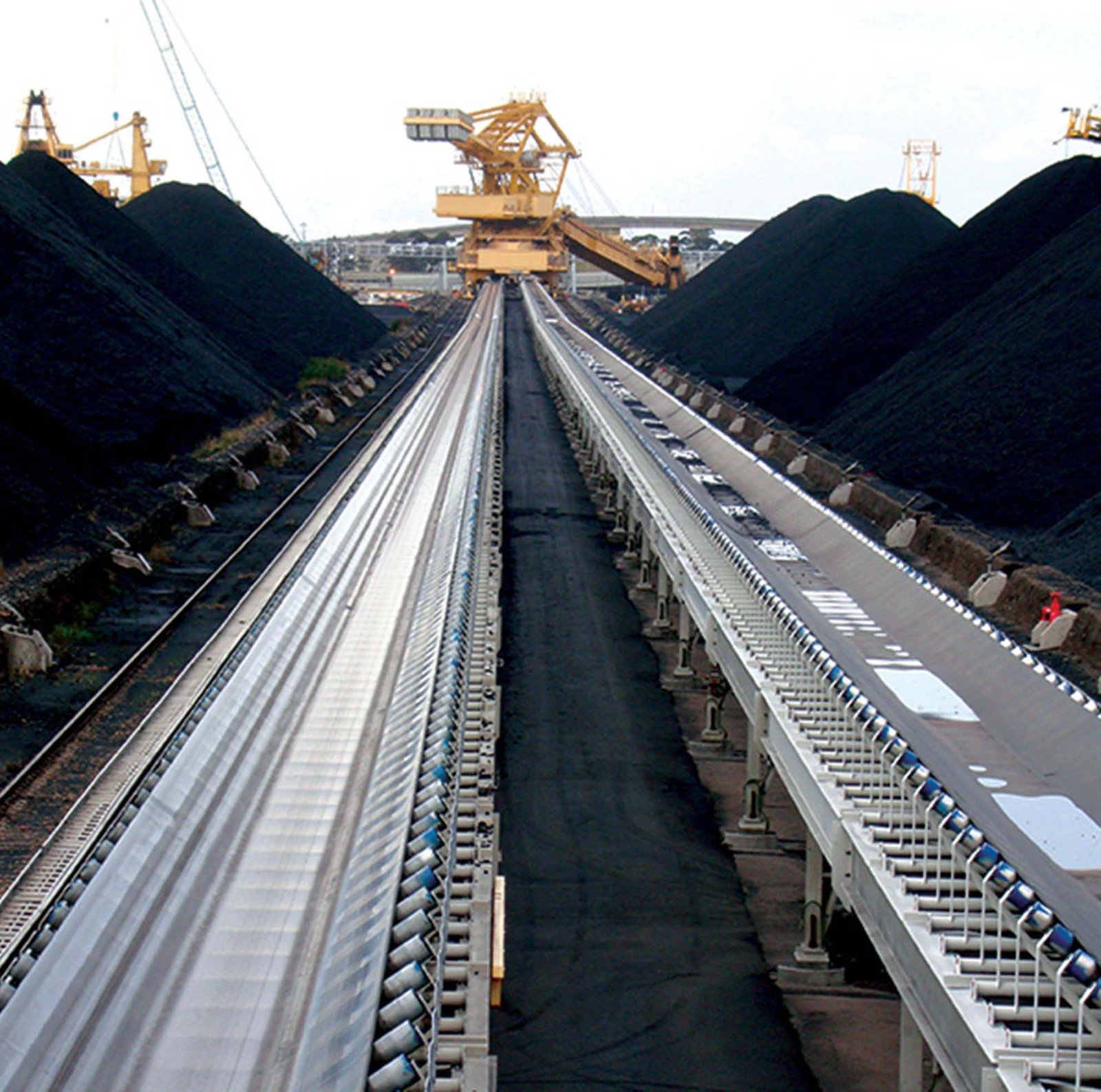

Coal is transported to thermal power plants as fuel for power generation. The transportation system needs to operate continuously and reliably to ensure the operation of the generator sets.
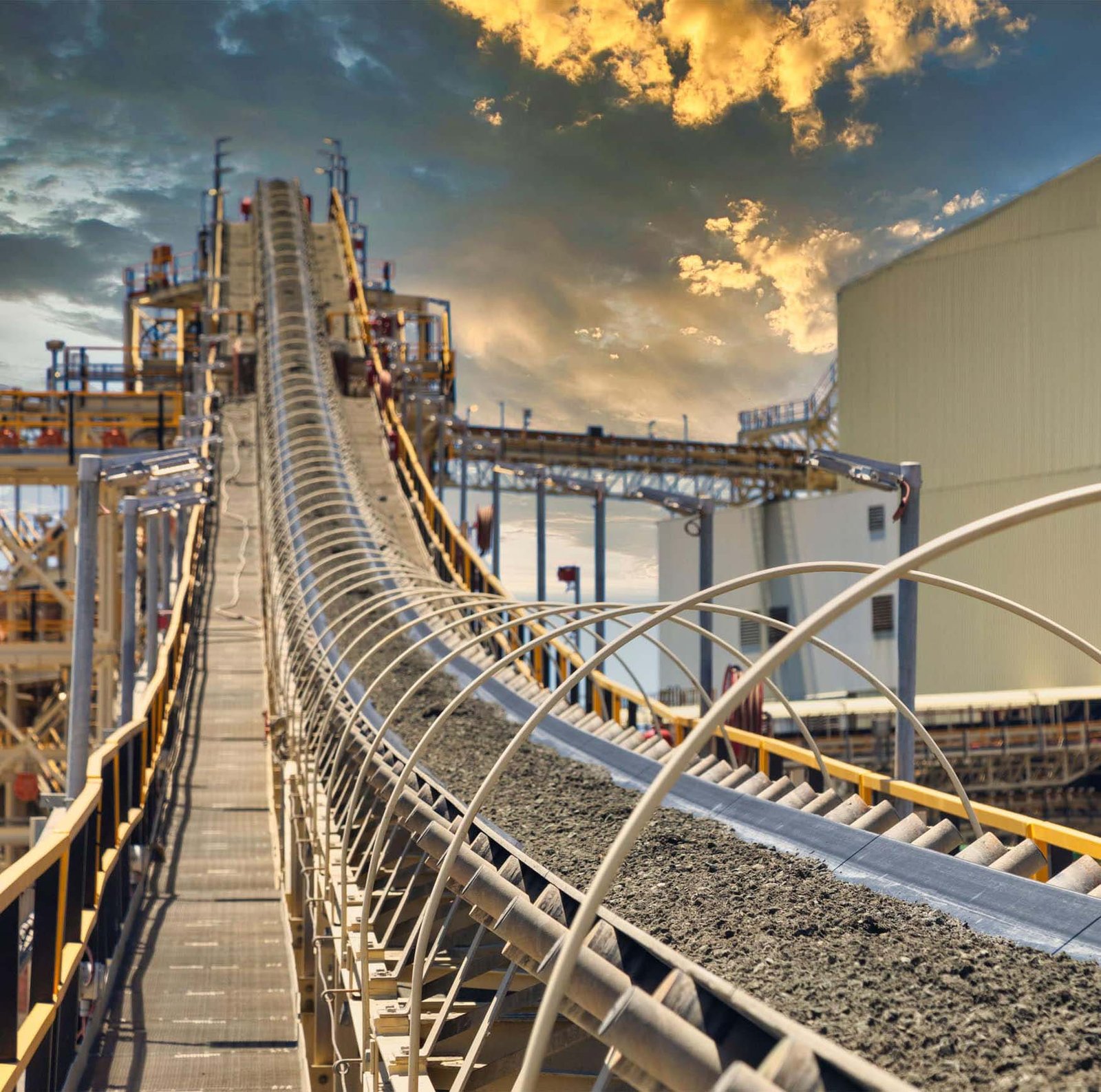

In the steel smelting process, it is used to transport high-temperature and sharp raw materials such as iron ore, sintered ore, and coke.
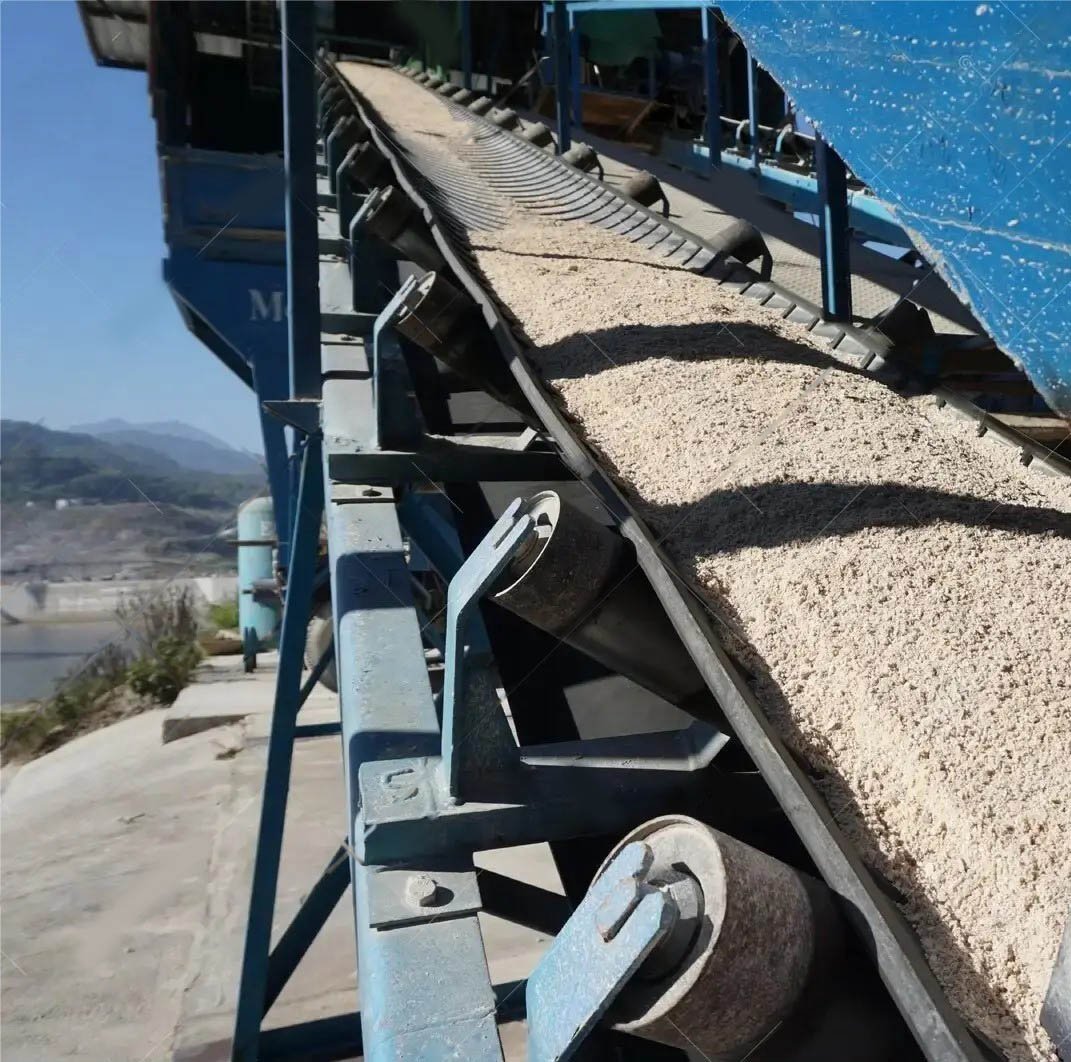

In the construction of large-scale water conservancy projects, construction materials such as sand, gravel, and aggregates need to be transported over long distances and large spans. Steel cord belts can adapt to complex terrain and achieve efficient and economical material supply.
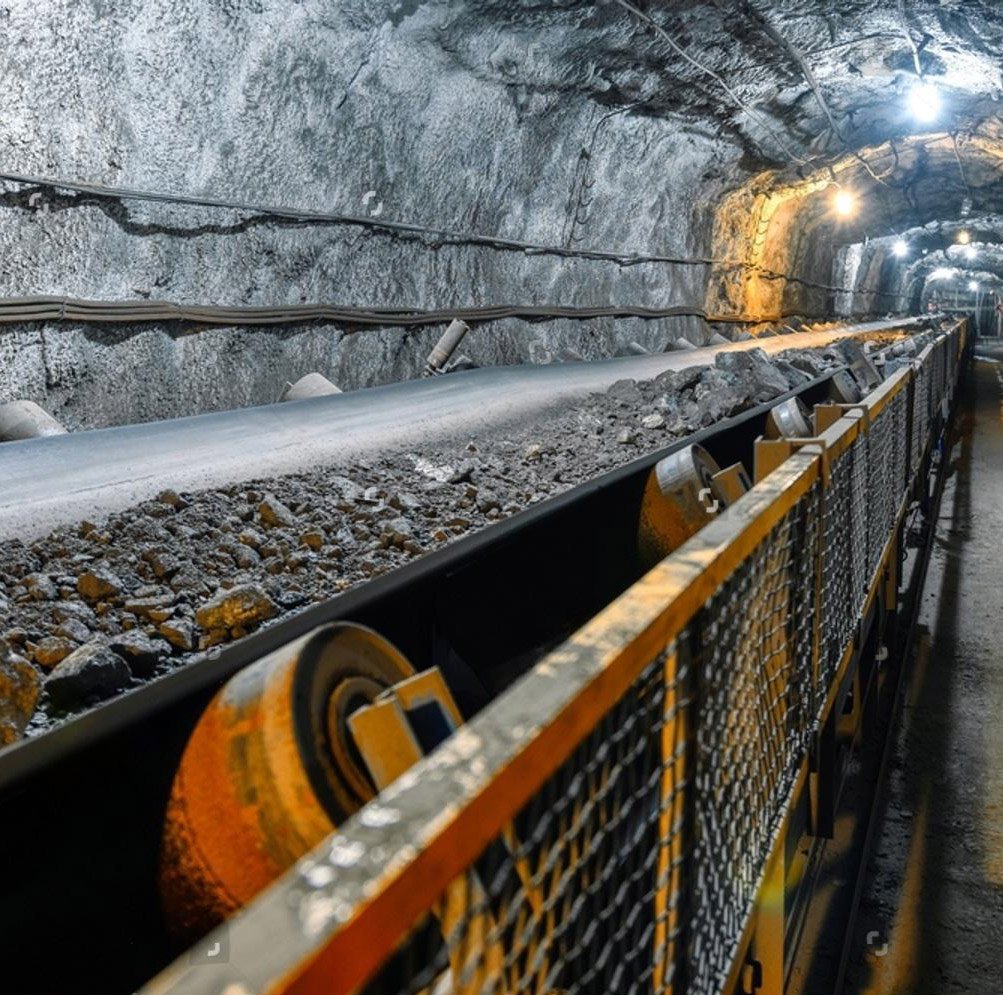

As the "lifeline" of coal mines from underground to the ground, this scenario requires the conveyor belt to have extremely high tensile strength to withstand the huge lifting height, and to be flame retardant and anti-static to ensure safety.
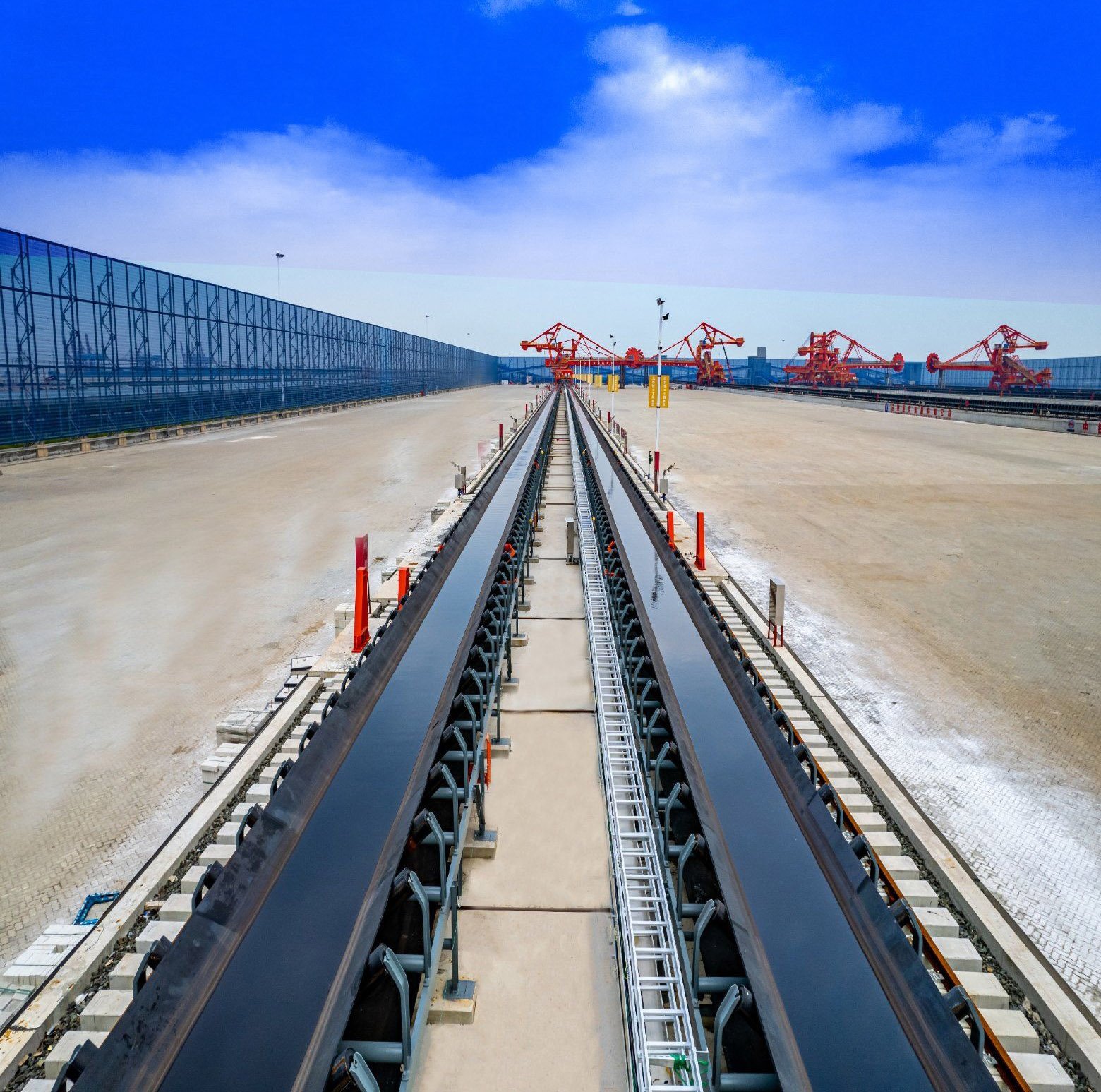

Used to connect storage yards and ships, it enables rapid loading and unloading of bulk cargoes such as coal, iron ore, and grain. Its high strength and impact resistance can withstand the impact of large grab buckets and continuous high-load operation, ensuring efficient and smooth port logistics.
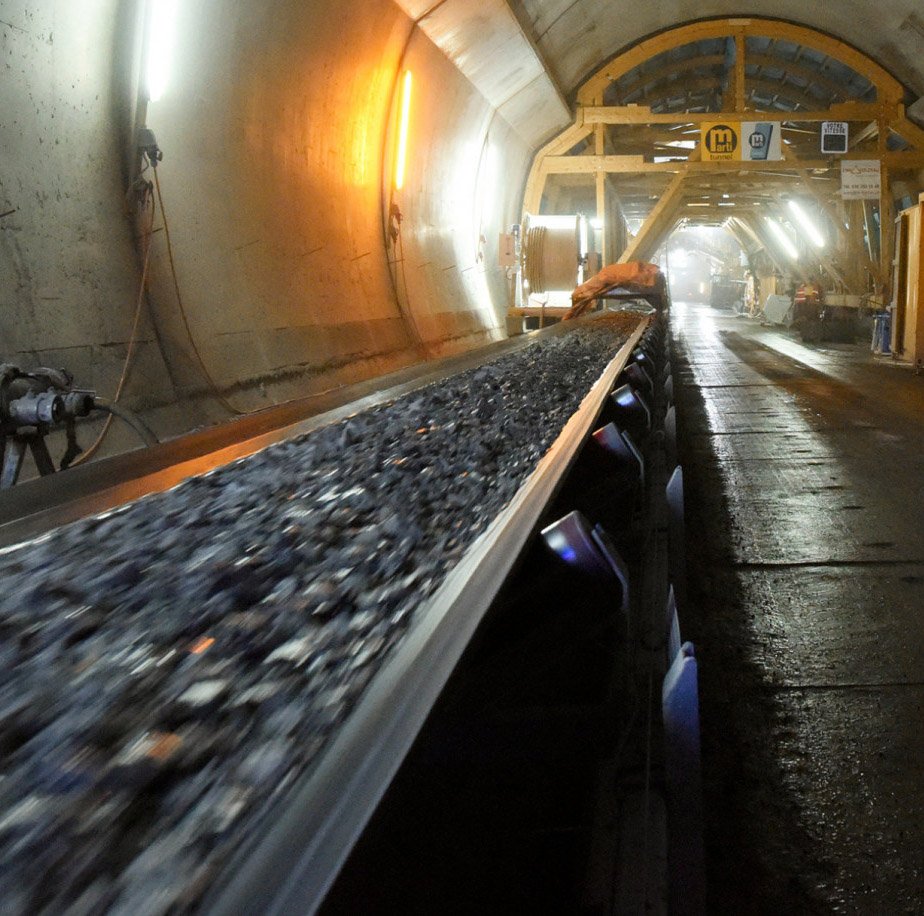

In projects such as mountain tunnels and water diversion tunnels, huge amounts of debris generated by shield machines or TBMs need to be continuously transported out of the tunnels.
You can get in touch with us through the following contact information
AddressNo. 2289 Huancheng South Road, Tongxiang, Jiaxing, Zhejiang Province, China. Zip code:314500
Please fill in the sales inquiry form and our sales representatives will be in touch shortly.